The Vagus Nerve: Gateway to Enhancing Memory and Learning
The brain processes and stores information through complex neural pathways, serving as the core organ for memory and learning. The vagus nerve contributes to this process by regulating cognitive and bodily functions, thereby influencing and potentially enhancing memory and learning mechanisms. Impairment of the vagus nerve can adversely affect these functions, leading to potential determinants in memory and cognitive abilities. Memory-related vagal impairment may be caused by chronic stress, trauma, PTSD, ADHD, hormonal imbalance, nutritional deficiencies¹, inflammation, viral infections², neurological conditions, obesity, depression and more³. This impairment can result in:
Stress Response
Parasympathetic activation via the vagus nerve has an anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effect by dampening the stress response. Vagus nerve impairment can induce chronic stress and influence memory and learning problems⁴.
Chronic Inflammation
Pro-inflammatory markers (like CRP, TNF-α, sICAM-1, sVCAM-1) are associated with inflammation in the body and increased risk of dementia. Dysregulation or impairment of the vagus nerve could exacerbate chronic inflammation, indicated by elevated levels of these markers, has been linked to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases⁵.
Neurotransmitter changes
Considering the importance of two brain chemicals: GABA and noradrenaline in neural plasticity and cortical excitability, impairment of the vagus nerve is believed to disrupt the balance of cerebral GABA and noradrenaline concentrations. Such dysfunction could potentially alter sequential behaviour, affecting both response selection and sequence learning components, due to the diminished regulation of these key neurochemicals⁶.
Neurogenesis Impairment
Dysfunction of the vagus nerve has been associated with reduced neurogenesis, or the production of new neurons, particularly in regions critical for memory and learning such as the hippocampus. This decrease in neurogenesis can hinder the formation of new memories, the ability to learn new information and the memory consolidation during sleep⁷.
- Jiang Y., Yabluchanskiy A., et al. (2022). The role of age-associated autonomic dysfunction in inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. GeroScience 44, 2655–2670.
- Verzele N.A.J., Short K.R., et al. (2023). Vagal Neuroinflammation Accompanying Respiratory Viral Infection: An Overview of Mechanisms and Possible Clinical Significance. In: Brierley, S.M., Spencer, N.J. (eds) Visceral Pain. Springer
- Tan C., Yan Q., et al. (2022) Recognizing the role of the vagus nerve in depression from microbiota-gut brain axis. Front. Neurol. 13, 1015175.
- Okonogi T., Kuga N., et al. (2024) Stress-induced vagal activity influences anxiety-relevant prefrontal and amygdala neuronal oscillations in male mice. Nat Commun 15, 183.
- Metti A.L., & Cauley J.A. (2012) How predictive of dementia are peripheral inflammatory markers in the elderly? Neurodegener Dis Manag. 1, 2(6), 609-622.
- Teleanu R.I., Niculescu A.G., et al. (2022). Neurotransmitters-Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci. 25, 23(11), 5954.
- O’Leary O. F., Ogbonnaya E. S., et al. (2018). The vagus nerve modulates BDNF expression and neurogenesis in the hippocampus. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 28(2), 307–316.
The Nurosym device has demonstrated activity on the parasympathetic system, contributing to a more favourable environment for cognitive processes. Nurosym's neuromodulation improves vagus nerve function, influencing multiple aspects of brain function and the parasympathetic nervous system, creating an environment conducive to memory formation and learning. Furthermore, parasympathetic activation is associated with better sleep quality, which can additionally impact sleep memory consolidation.
Nurosym device was proven to modulate the body’s inflammatory response, which may potentially improve cognition. Neuromodulation technique engages the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, a mechanism where the vagus nerve inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α. By reducing the systemic inflammation, Nurosym can mitigate the inflammatory impact on the brain. This decrease in inflammation can lead to a healthier neural environment, preserving neuronal function and reducing risk of cognitive decline and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Nurosym activates the vagus nerve, potentially improving cognitive function by balancing brain chemistry. Stimulation of the vagus nerve can increase neurotransmitter levels, influencing behavior. Research suggests that the vagus nerve communicates with the brain. The locus coeruleus (LC) contains the largest population of noradrenergic neurons in the brain and receives projections from the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS), which, in turn, receives afferent input from the vagus nerve. Hence, Nurosym could potentially boost the activity of noradrenergic (NE) neurons, subsequently leading to an increase in serotonin neuron firing. These chemical changes streamline neural selection, supporting optimal cognitive function and potentially addressing scattered cognitive symptoms linked to memory loss.
The impact of the Nurosym device on sequential learning and response selection processes involving key brain areas was examined. The Nurosym test indicated a positive effect, likely due to neuromodulation enhancing consolidation processes potentially via the hippocampus, and contribution to improved memory consolidation during sleep. Due to activation of the vagus nerve Nurosym has the potential to alter activation patterns in specific brain areas (hippocampus, parahippocampus, amygdala, anterior cingulate cortex, and prefrontal cortex). These changes imply improved functionality in brain regions crucial for cognitive control, motor learning, memory consolidation and emotional regulation.
Nurosym Research-Based Evidence
73% of users noted improved cognition and memory after Nurosym therapy, demonstrating significant enhancements in dementia symptoms and overall productivity.
In clinical trials, participants were assessed at three key time points: baseline (Day 0), post-intervention (Day 10), and at a 1-month follow-up. The intervention led to significant cognitive improvements, with performance in Flanker Inhibitory Control and Attention increasing by 11%, and overall Fluid Cognition improving by 17%.
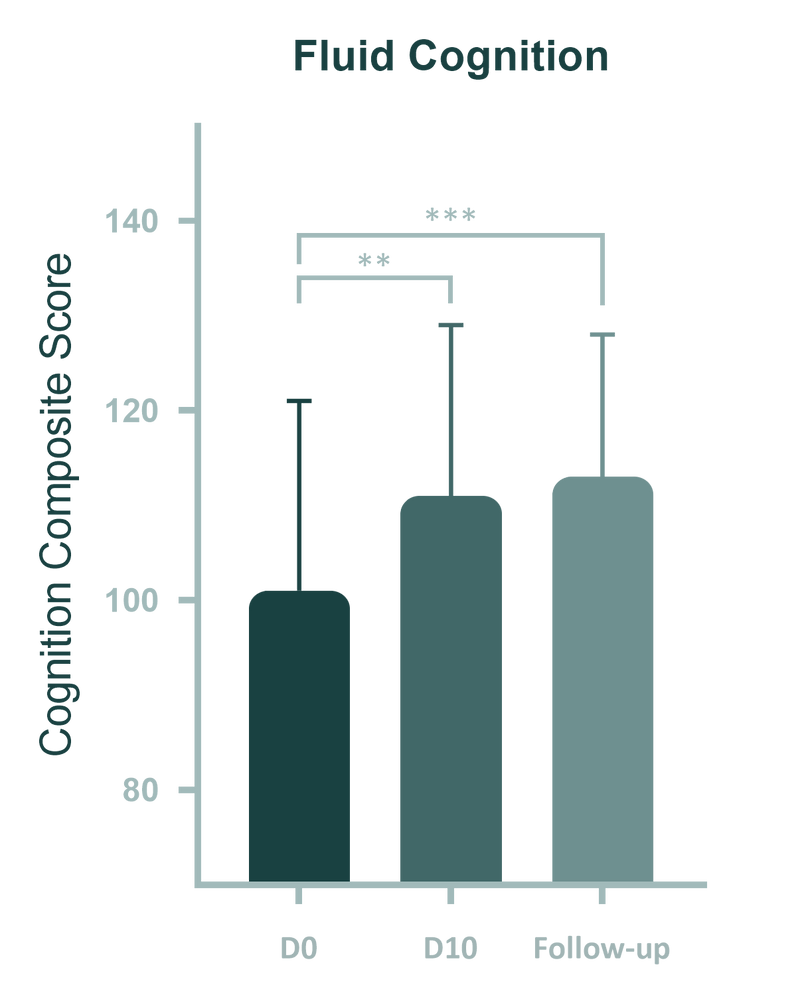
(Fig). The Fluid Cognition Score represents cognitive performance across several domains, including Pattern Comparison Processing Speed, Pattern Sequencing Memory, and List Sorting Working Memory. The study showed significant increases from baseline to post-intervention and follow-up (p < 0.01). Friedman’s test indicated a significant main effect of time (p = 0.001) across all composite cognitive scores (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2024).
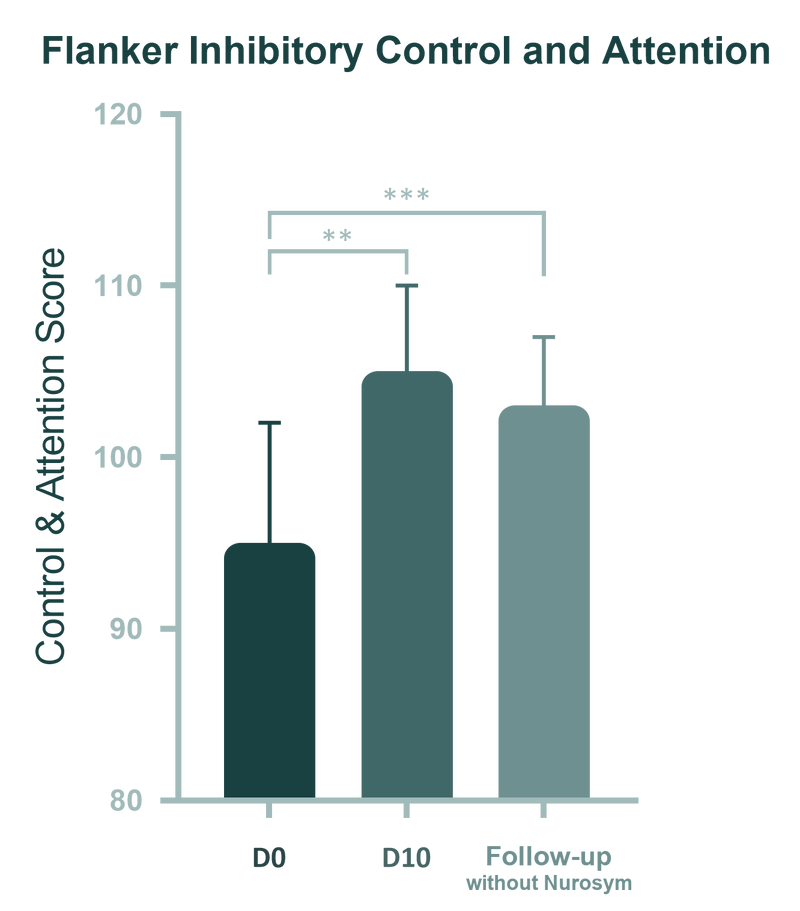
(Fig). Participants were tested at three points: baseline (Day 0), post-intervention (Day 10), and 1-month follow-up. Significant improvements were found in Flanker Inhibitory Control and Attention from baseline to post-intervention (p = 0.009) and follow-up (p < 0.001).
In clinical trials patients within 5 days demonstrated 32% enhanced memory and 26% learning performance with Nurosym, showing significant improvements in both speed and accuracy on various cognitive tasks compared to placebo.
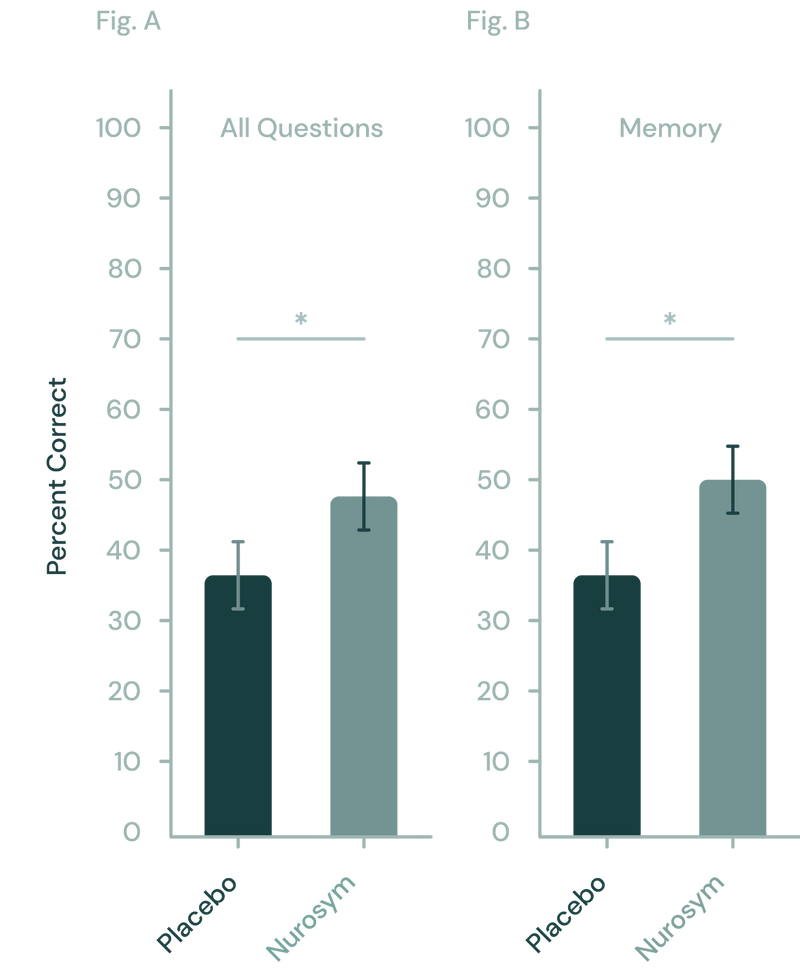
Fig (A, B). Nurosym has shown to enhance memory in learning tasks relative to a placebo. (A) Across all test questions, Nurosym's neuromodulation demonstrated a notable advantage over placebo. (B) Specifically, this improvement was largely due to the significant impact of Nurosym neuromodulation on memory-related questions (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2020).
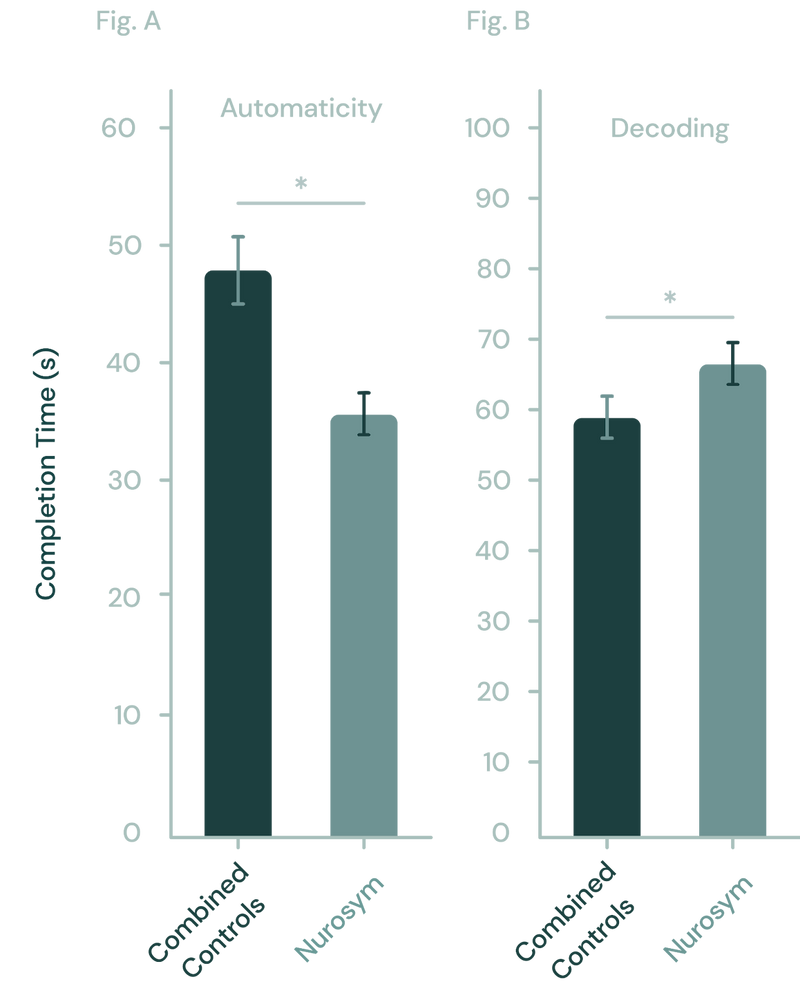
Fig (A, B). In the study, pairing Nurosym neuromodulation with training notably enhanced speed performance in the Automaticity learning task (significantly, *p<0.05), compared to placebo controls. Additionally, Nurosym neuromodulation significantly improved accuracy, as measured by the percent correct, in the Decoding learning task when compared to controls (*p < 0.05) (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2020).
Brain fog is often associated with sympathetic activity. Enhancement in HRV (up to 61% in HF power) during Nurosym therapy suggests a positive impact on reducing sympathetic activity and is associated with cognitive improvement.
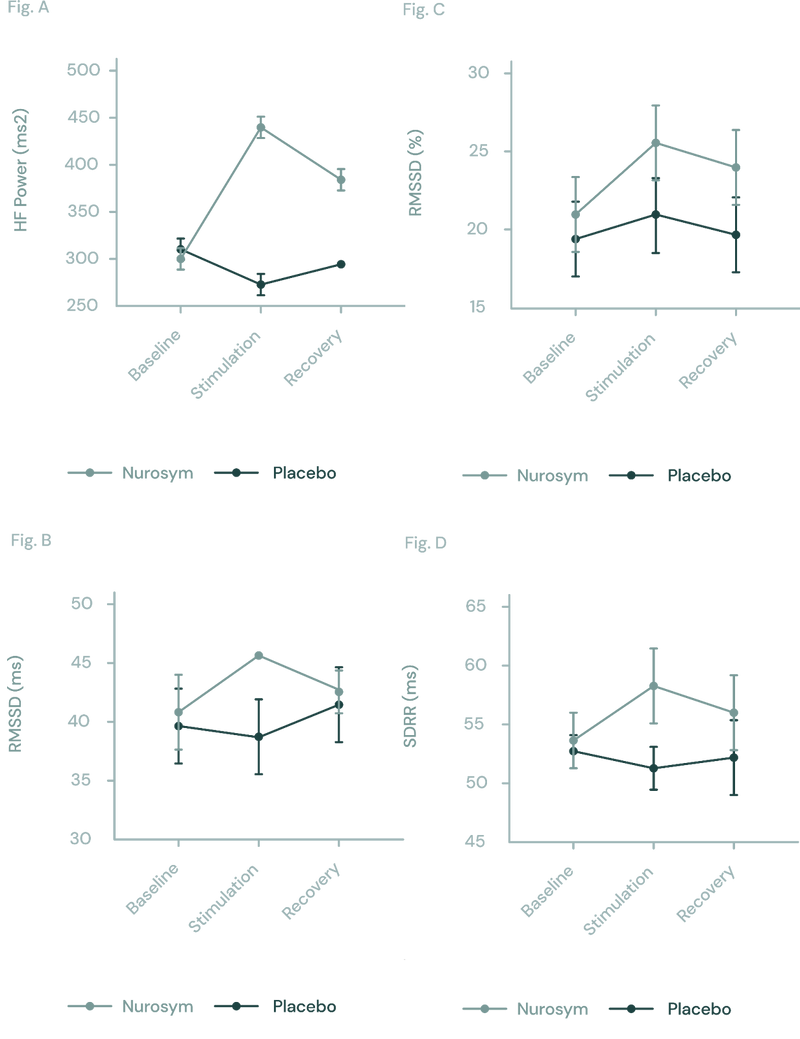
Fig (A, B, C D). The response of autonomic function measured by HRV in Nurosym or Placebo conditions over time: (A) HF, (B) RMSSD, (C) pRR50, (D) SDRR. With Nurosym, the measurements of HF, RMSSD, PRR50 and SDRR were significantly higher than those in Placebo (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2022).
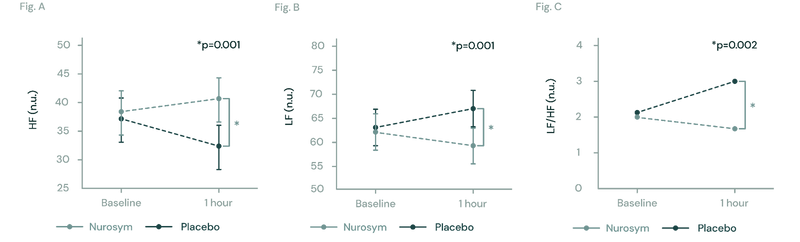
Fig (A, B, C). The figures illustrate changes in heart rate variability (HRV) during Nurosym neuromodulation. In Figure (A), High Frequency HRV significantly increases (*p=0.001). In Figure (B), Low Frequency HRV significantly decreases (*P=0.001). Figure (C) demonstrates that the ratio of LF to HF is significantly decreased (*p=0.002) (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2018).
In clinical trials, after Nurosym neuromodulation, patients experienced even a 78% decrease in inflammatory cytokine levels (IL-6), reflecting the reduction of inflammatory processes in the brain.
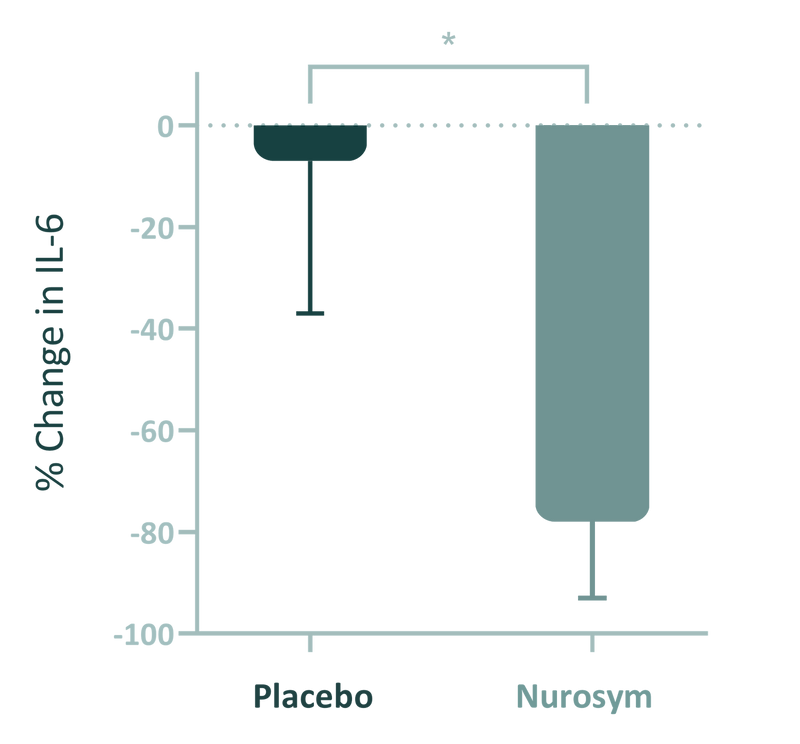
(Fig). The results demonstrate that Nurosym effectively reduced systemic inflammation. Specifically, vagus nerve stimulation resulted in a significant decrease in interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels, with a reduction of 78.48% in the Nurosym group compared to just 8.63% in the control group (p = 0.012) (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2023)
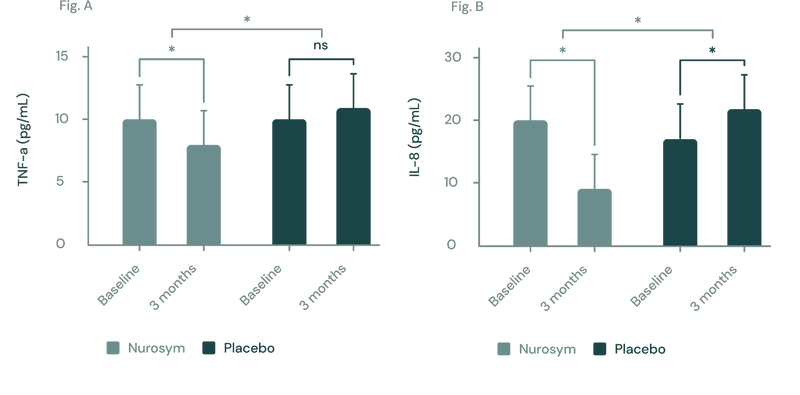
(Figure A, B) In a three-month study employing the Nurosym device for heart failure patients, notable improvements (*P<0.05) were noted in inflammatory biomarkers: (A) Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)‐α exhibited a ~23% reduction, while (B) Interleukin (IL)‐8 showed a marked ~61.3% reduction. The investigation specifically targeted participants with elevated baseline inflammation levels (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2022).
Doctors about Nurosym
Patients about Nurosym
Yvonne
“I've been using the Nurosym device since January 2021. I use it every day for an hour and sometimes I achieve even more concentration. Sometimes I'll read a book while I've got it on. And I find that I'm able to concentrate sometimes on quite difficult pieces of writing.”
Who is for it?
Nurosym is particularly beneficial for individuals seeking alternative or adjunctive solutions for cognitive impairment or those aiming to enhance their memory without relying on traditional pharmaceuticals, or to achieve better results with combination therapies.
Given the complexities of conditions related to cognitive impairment and the potential side effects of certain drugs, neuromodulation therapy presents a promising, non-invasive option.
It is frequently recommended by researchers and clinicians for individuals experiencing mild to moderate memory decline, particularly in connection with anxiety episodes, to improve cognitive function without additional medications.
Protocol - How to Use
For enhanced learning and memory consolidation, apply Nurosym by attaching the device to the tragus on the ear (where fibres of the vagus nerve are present) for one hour during study sessions, starting 5 minutes prior to optimise cognitive function. Individuals with dementia or motor impairments should use the device for up to 4 hours daily, in divided sessions for maximum benefit. Applying Nurosym before sleep may enhance memory consolidation.
How often
Nurosym is recommended for use twice daily based on clinical research and patient feedback. This regimen ensures optimal energy balancing and nervous system calming.
How long
Users should allocate 30 minutes in the morning and 60 minutes before sleep for Nurosym therapy sessions. Consistency in application is key to achieving desired results.
Results
Positive outcomes from Nurosym therapy may become noticeable within a relatively short timeframe. Many individuals report improvements within days of starting treatment.


