Scientific Evidence
Nurosym is pioneering a new class of technology that uses bioelectrical signals targeted to neural circuits of organs, treating disease without surgery or drugs.
-
67% increase in 5 minutes
Vagus Nerve Activity
-
90% increase after 2 mo.
Vagus Nerve Activity
-
35% reduction
Anxiety
-
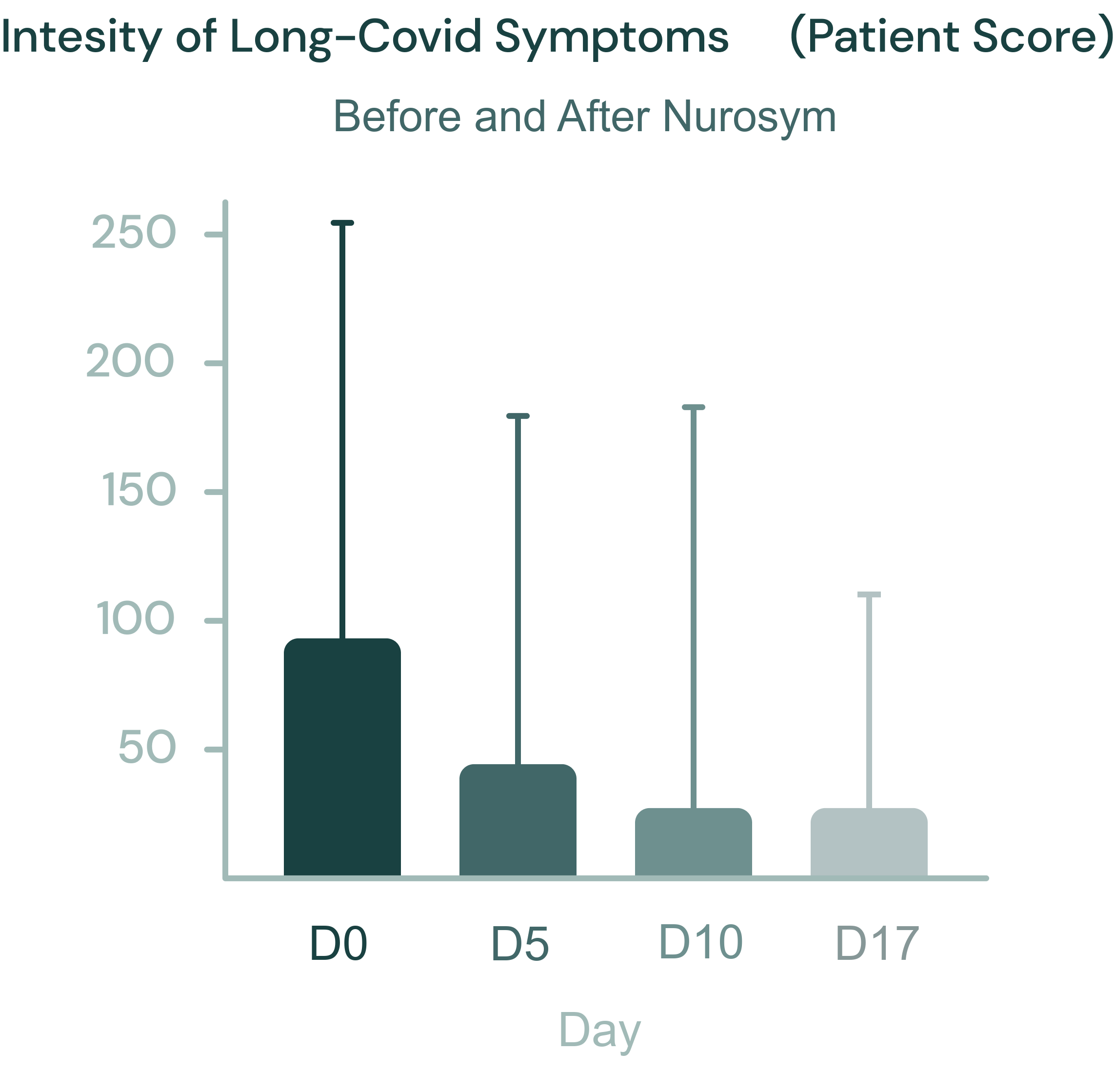
61% reduction
Long-Covid Symptoms
-
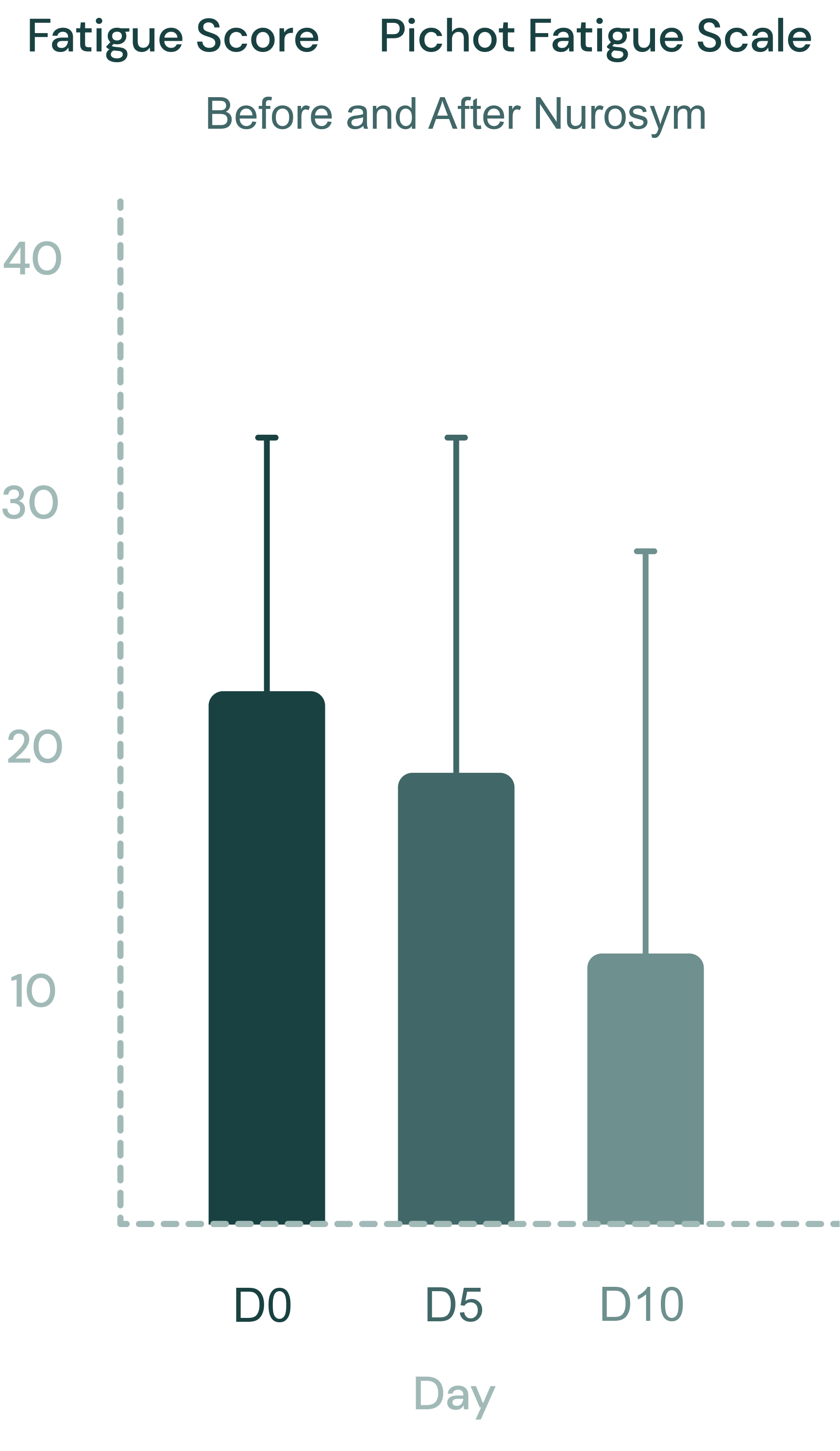
48% reduction
Fatigue
-
31% improvement
Sleep Quality
-
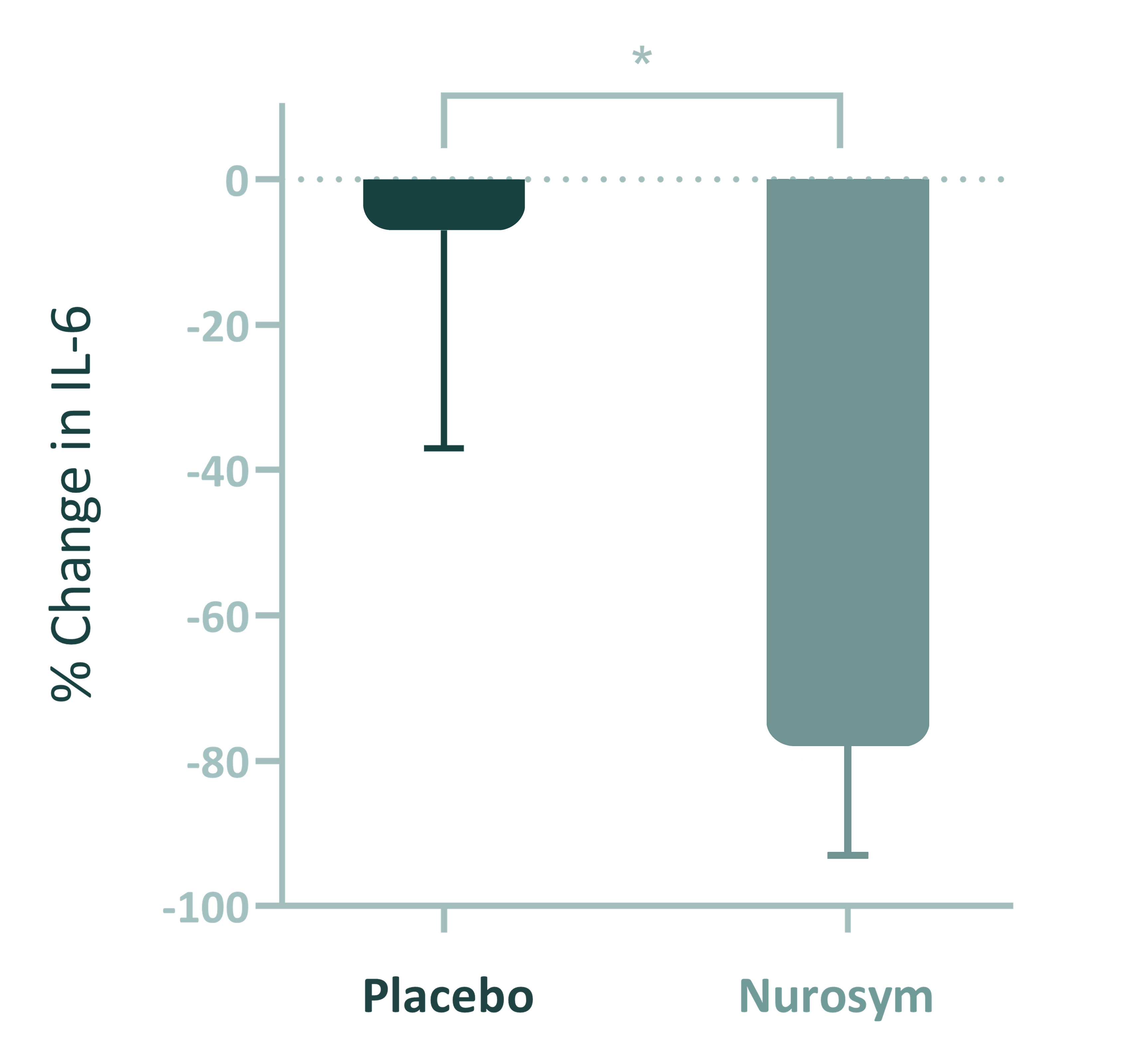
78% reduction
Inflammation
-
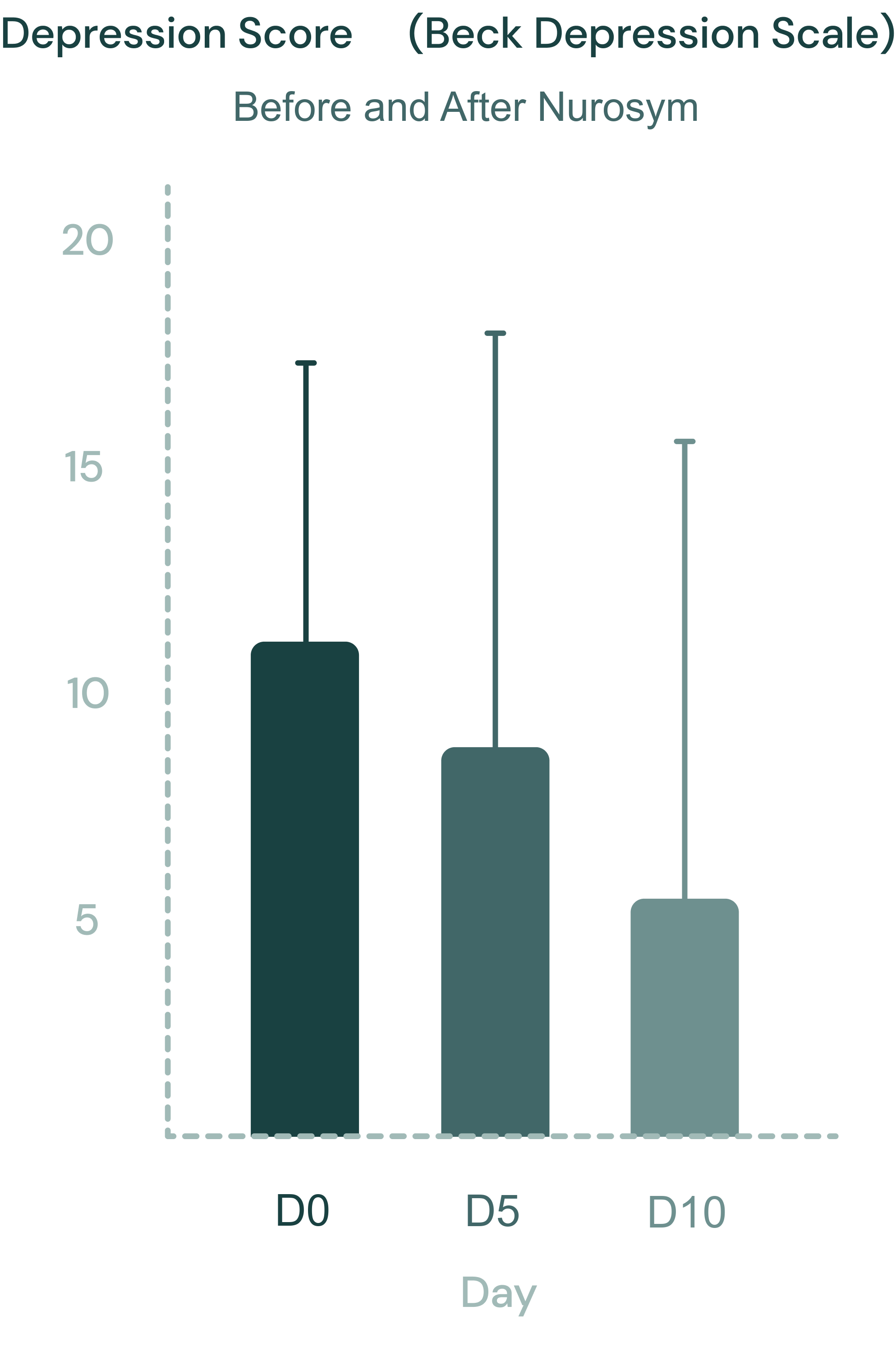
45% reduction
Depression Symptoms
-
18% increase
Heart Rate Variability
-
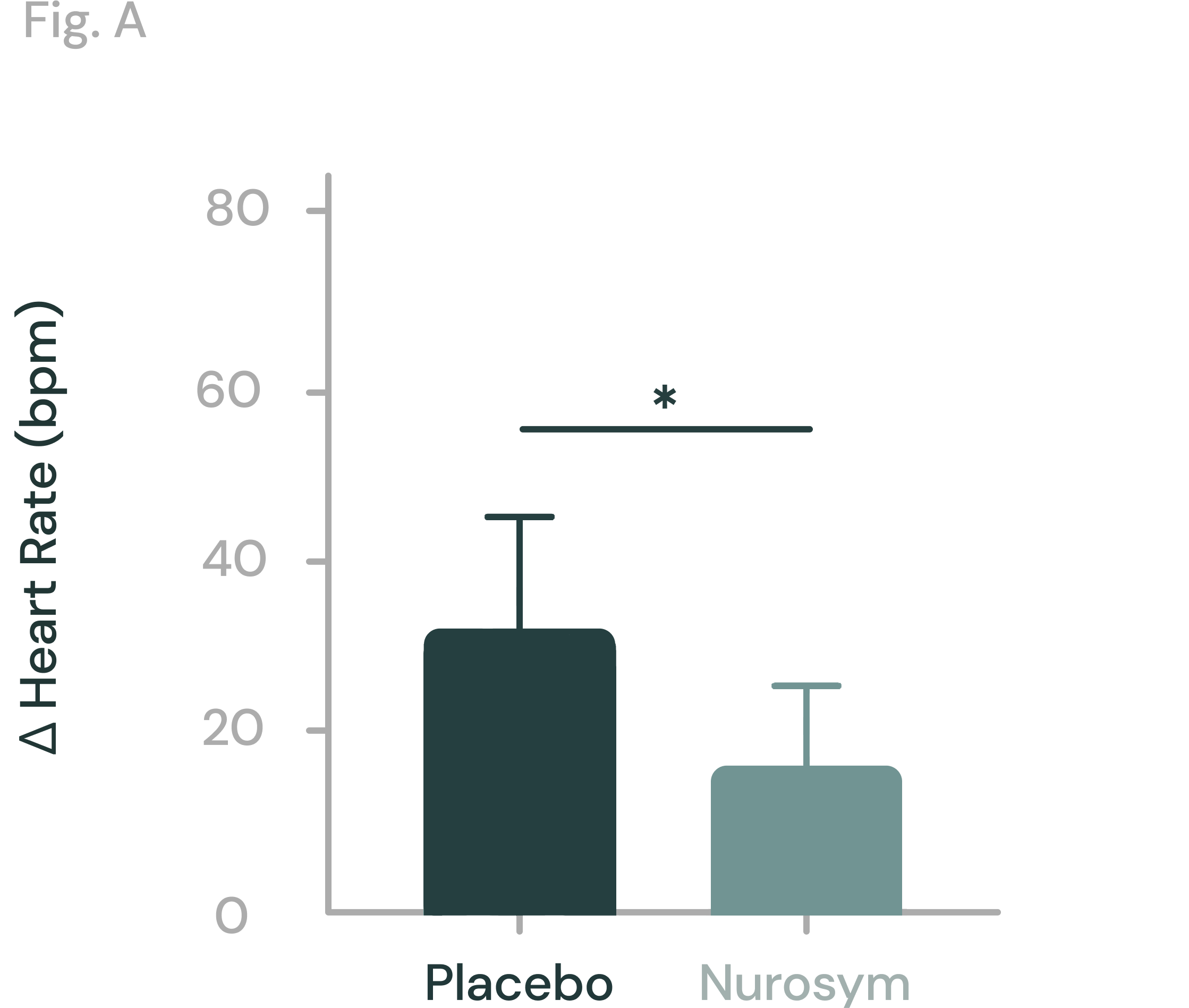
40% reduction
POTS Tachycardia
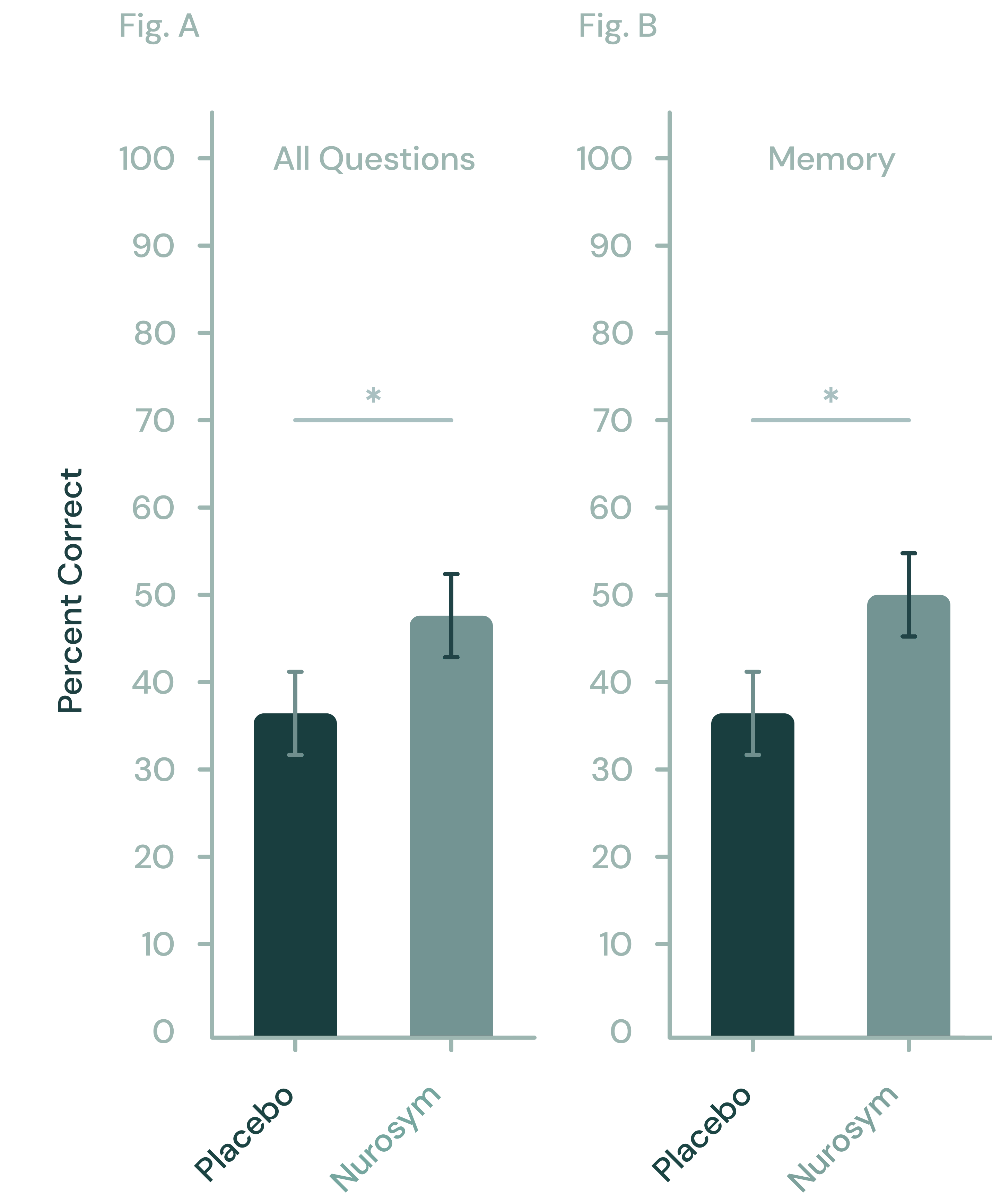
-
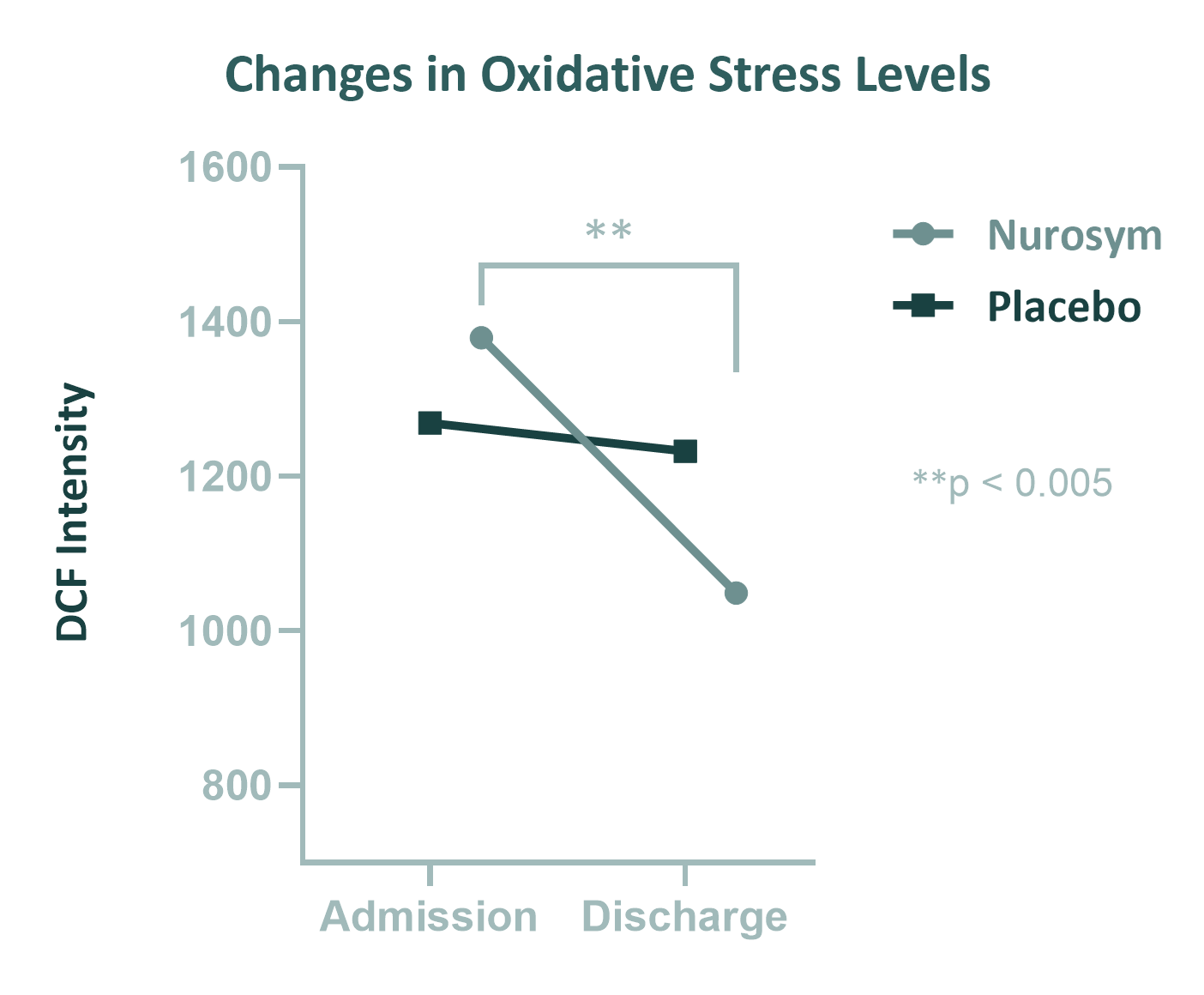
28% reduction
Oxidative Stress
-
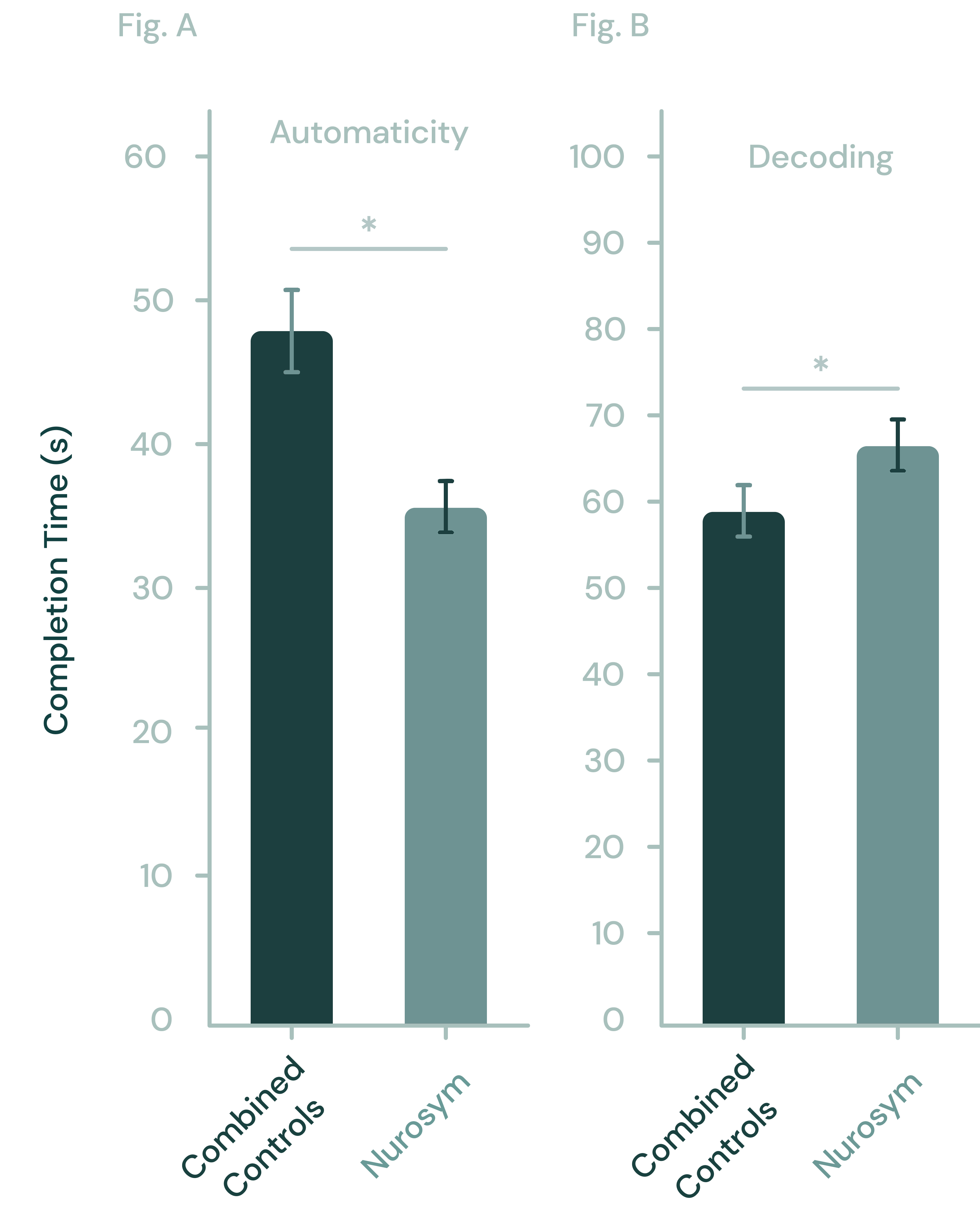
32% improvement
Memory
-
29% improvement
Reading
-
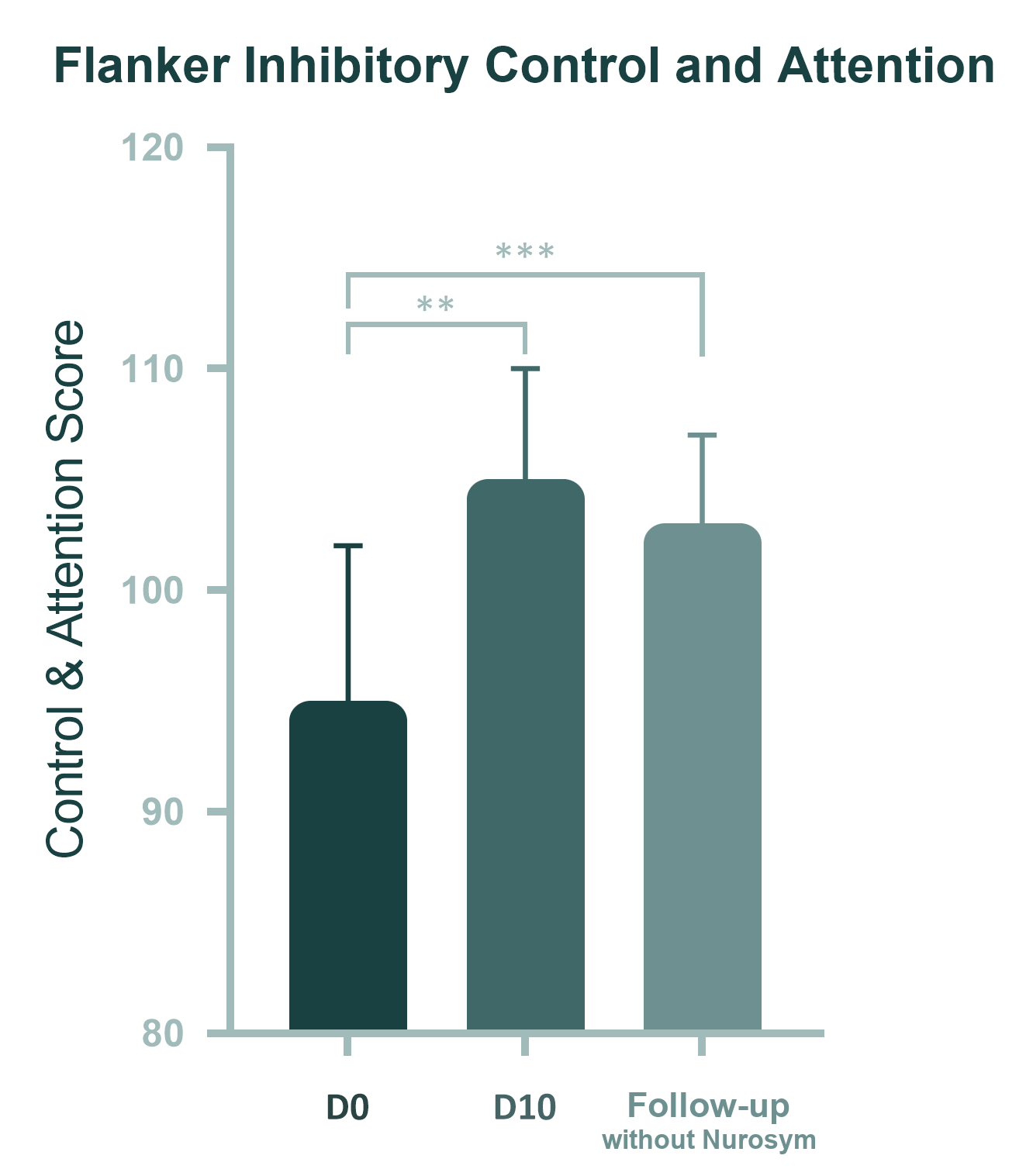
11% reduction
Attention Deficiency
-
50% improvement
Macrocirculation
-
39% improvement
Microcirculation
-
10% reduction
Blood Pressure
-
27% improvement
Fibromyalgia Symptoms
-
36% improvement
Widespread Pain
-
Results in specific study populations. Individual results may vary.
-
SHOP NUROSYM See Scientific Evidence
30 Day Money-Back Guarantee
If you try Nurosym for 30 days and aren’t happy with your results, we’ll send you a full refund
Nurosym Results from 50+ Clinical Trials
Nurosym sends patented electrical impulses to the brain via the Vagus Nerve, which leads to:
Cutting edge Neuromodulation
With a simple wearable device
50+
Ongoing clinical studies
4M+
Happy patient sessions
30
Day money back guarantee
Certified medical device