Vagus Nerve and Its Role in Alleviating Brain Fog
The vagus nerve, integral to the parasympathetic nervous system, regulates brain-body communication, influencing mental clarity and cognitive function. Brain fog can be affected by the vagus nerve, responsible for maintaining the balance of neurotransmitters, ensuring proper brain function, and regulating the response to stress. Dysfunction or decreased vagal tone can disrupt these processes, leading to decreased cognitive performance, attention, and memory. Damage to the vagus nerve causing brain fog may result from medications intake, stress, hormonal imbalance, poor diet¹ anaemia, inflammation, viral infections², sleep apnea³, or depression⁴ – influences often associated with brain fog:
Stress Response
Chronic stress leads to sympathetic overstimulation, which in turn can diminish the regulatory capacity of the vagus nerve over bodily functions. This weakening contributes to cognitive impairments commonly associated with brain fog. Furthermore, such stress can cause dysregulation of the HPA axis—a key stress response system—resulting in an excessive or prolonged release of cortisol and other stress hormones, further impacting cognitive function⁵.
Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory markers (CRP, TNF-α, sICAM-1 and sVCAM-1) are associated with body inflammation and an increased risk of brain fog. Dysregulation or impairment of the vagus nerve may contribute to exacerbation of chronic inflammation, as indicated by elevated levels of these markers. This increased inflammation has been linked to cognitive decline and symptoms of brain fog doi.
Optimal vagal tone is crucial for maintaining focus, memory, and mental clarity. Abnormal vagus nerve functioning seems to be involved in affective disorders, as indicated by altered frontal–vagal network in the brain. Disruption in the vagal network can lead to scattered thoughts and diminished cognitive function, characteristic of brain fog.
The vagus nerve, integral to the neuroendocrine-immune axis, connects the Central Nervous System (CNS) with the intestinal immune system. Chronic infections or immune responses can impair its signalling, leading to decreased production of neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, exacerbating brain fog symptoms by disrupting cognitive and emotional regulation.
- Jiang Y., Yabluchanskiy A., et al. (2022). The role of age-associated autonomic dysfunction in inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. GeroScience 44, 2655–2670.
- Verzele N.A.J., Short K.R., et al. (2023). Vagal Neuroinflammation Accompanying Respiratory Viral Infection: An Overview of Mechanisms and Possible Clinical Significance. Visceral Pain, Springer.
- Guo Y., Xiaokereti J., et al. (2021). Low-Level Vagus Nerve Stimulation Reverses Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Related Atrial Fibrillation by Ameliorating Sympathetic Hyperactivity and Atrial Myocyte Injury. Front. Physiol. 11:620655.
- Tan C., Yan Q., et al. (2022). Recognizing the role of the vagus nerve in depression from microbiota-gut brain axis. Front. Neurol. 13:1015175.
Nurosym normalises the autonomic nervous system, reducing sympathetic overactivity and enhancing parasympathetic activity, thereby mitigating the physiological effects of stress on cognitive function. Nurosym, with its anti-inflammatory effects, influences the HPA axis and improves cell stress resilience for cortisol release. These combined effects can improve cognitive function and potentially alleviate brain fog symptoms.
The Nurosym device helps control the body’s inflammation, potentially benefiting cognitive function. Through neuromodulation, it activates the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, where the vagus nerve plays a role in modulation inflammation, and therefore reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α. By reducing overall inflammation, Nurosym can lessen its impact on the brain, thereby protecting against cognitive decline and symptoms associated with brain fog.
Nurosym is thought to induce chemical changes in monoamine metabolism by reducing inflammation in the gut-brain axis. This process may enhance the absorption of tryptophan and tyrosine, amino acids responsible for neurotransmitter production in the intestines. Serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine are crucial neurotransmitters that play a role in cognitive regulation. Modulating the concentrations of these neurotransmitters could potentially contribute to therapeutic benefits, especially in addressing issues like brain fog (doi: 10.51956/ANNR.100011; doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01159).
Neuronal Plasticity Enhancement
Through repeated stimulation, Nurosym activates vagus nerve fibres, improving vagal tone measured by Heart Rate Variability (HRV) which may influence brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels, a crucial marker for neuroplasticity and the promotion of neuron production. Research suggests that the vagus nerve may propagate to higher brain structures involved in cognitive functions, including the hippocampus, insula, prefrontal cortex, and motor cortex. This process enhances neuronal plasticity and potentially reduces cognitive symptoms associated with brain fog (doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2023.04.051; doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04639-1)..
Nurosym Research-Based Evidence
71% of patients using Nurosym reported a decrease in brain fog symptoms, leading to mood improvement and a reduction in future-related stress within just 10 days.
After 2 weeks of Nurosym neuromodulation therapy, patients experienced an average of 57% improvement in cognition related to symptoms of brain fog, as evidenced in clinical trials (doi: 10.1101/2022.11.08.22281807).
Another Nurosym finding highlights significant remission by 40% of debilitating symptoms, including brain fog, in all long-COVID patients included in the study (doi: 10.51956/ANNR.100011).
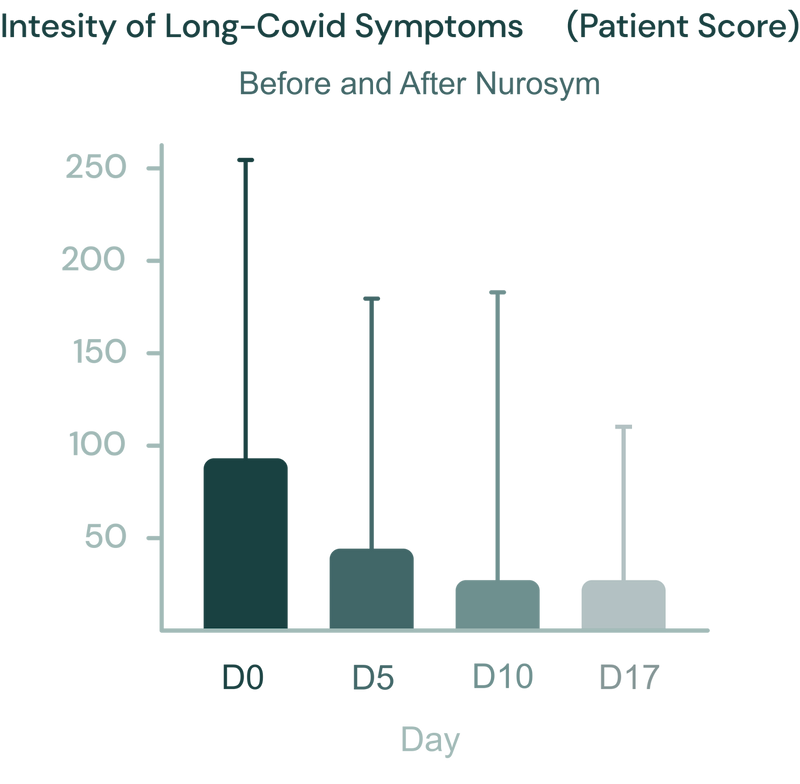
Fig. Evolution of the severity of the syndrome, during treatment (day 0, day 5, day 10), and 1 week after ending Nurosym neuromodulation (follow-up). The individual values and the median are shown. Non parametric Friedman statistics for paired comparisons were used and followed by post-hoc Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.51956/ANNR.100011).
Brain fog, often described as slow thinking, and in clinical trials patients within 5 days demonstrated 32% enhanced memory and 26% learning performance with Nurosym.
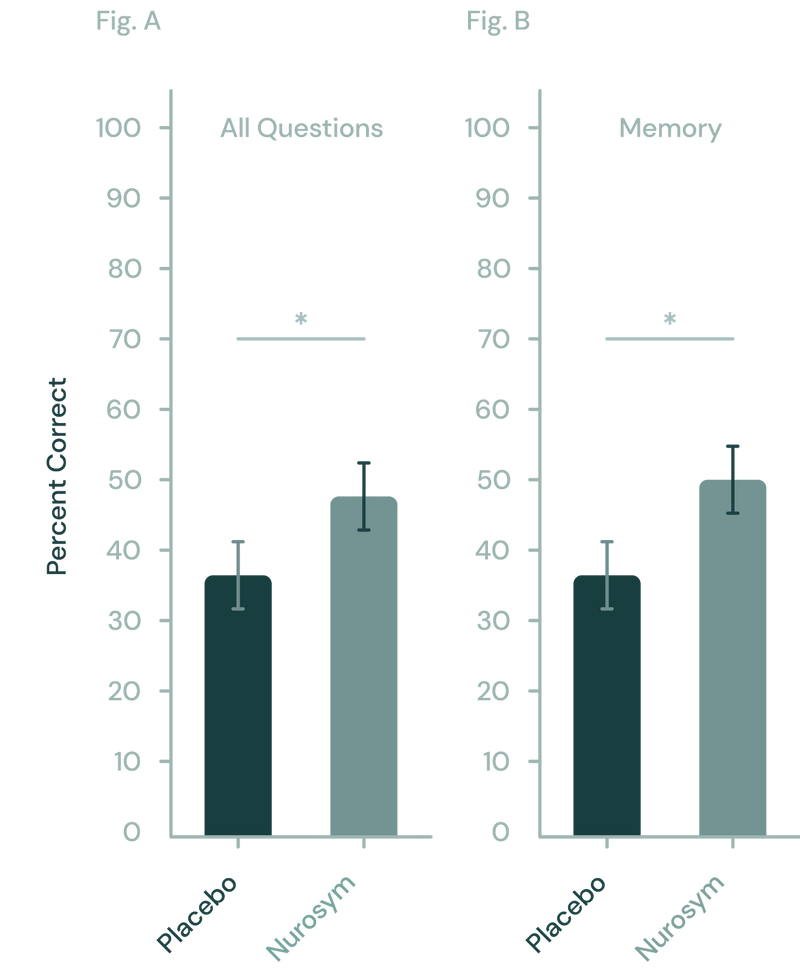
Nurosym has shown to enhance memory in learning tasks relative to a placebo. (A) Across all test questions, Nurosym's neuromodulation demonstrated a notable advantage over placebo. (B) Specifically, this improvement was largely due to the significant impact of Nurosym neuromodulation on memory-related questions (doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2020.10.012).
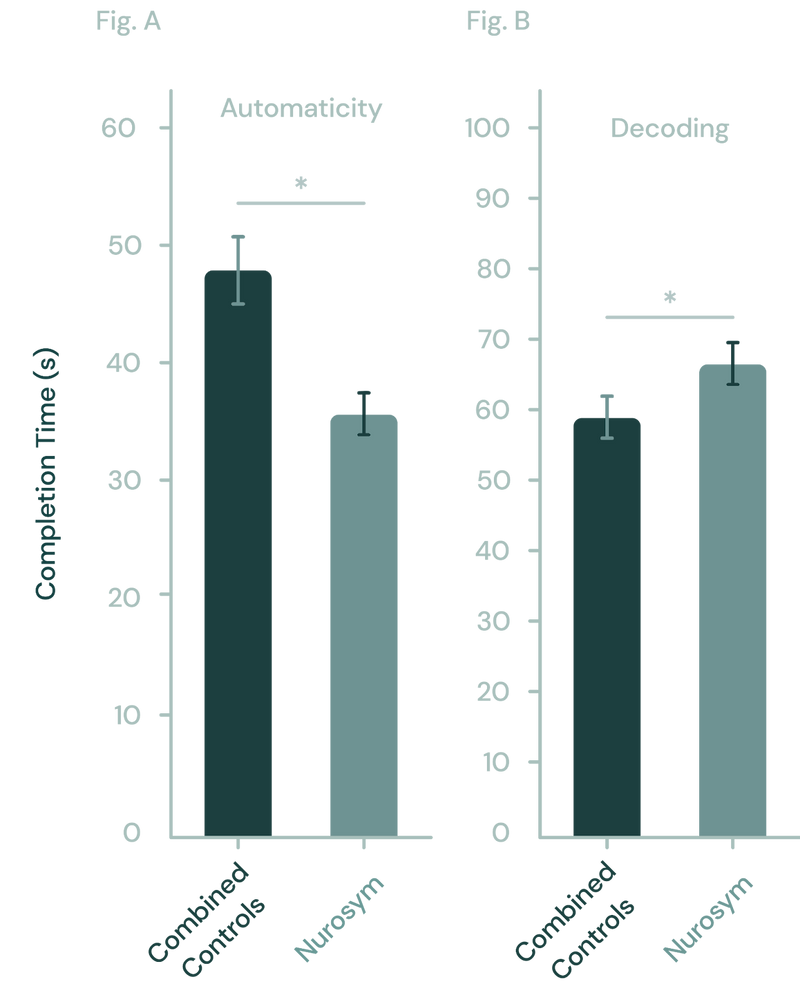
In the study, pairing Nurosym neuromodulation with training notably enhanced speed performance in the Automaticity learning task (significantly, *p<0.05), compared to placebo controls. Additionally, Nurosym neuromodulation significantly improved accuracy, as measured by the percent correct, in the Decoding learning task when compared to controls (*p < 0.05) (doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2020.10.012).
Reduced HRV is associated with worse performance in cognitive domains. Patients using Nurosym observed enhancements in their HRV and the research has indicated 61% improvement (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263833).
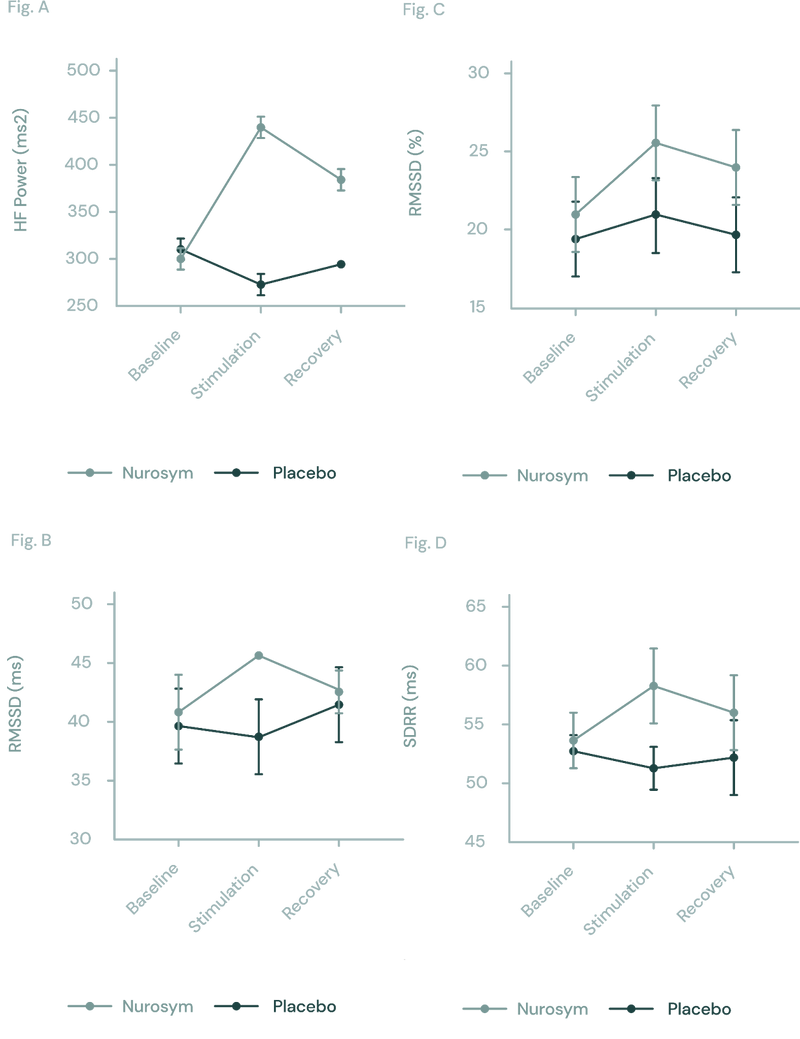
Fig (A, B, C D). The response of autonomic function measured by HRV in Nurosym or Placebo conditions over time: (A) HF, (B) RMSSD, (C) pRR50, (D) SDRR. With Nurosym, the measurements of HF, RMSSD, PRR50 and SDRR were significantly higher than those in Placebo (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263833).
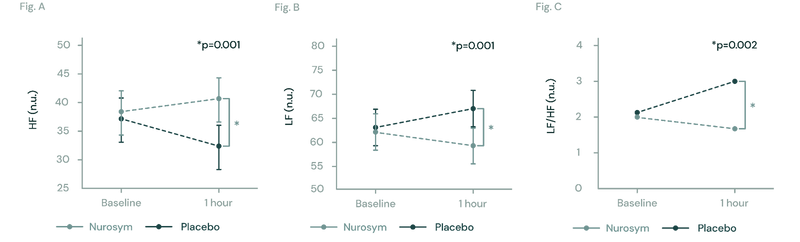
Fig (A, B, C). The figures illustrate changes in heart rate variability (HRV) during Nurosym neuromodulation. In Figure (A), High Frequency HRV significantly increases (*p=0.001). In Figure (B), Low Frequency HRV significantly decreases (*P=0.001). Figure (C) demonstrates that the ratio of LF to HF is significantly decreased (*p=0.002) (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263833).
Doctors about Nurosym
Patients about Nurosym
Tatiana
“Nurosym considerably helped soothe the multiple inflammatory conditions I had developed after covid, such as arthritis, myocarditis, thyroiditis and brain fog. As I now feel better, I do not need to use it every day anymore, but I still incorporate it in my routine whenever I feel the need to relax and restore my nervous system and my whole body.”
Nick
“I have been prescribed mood medication which is sedating. Unfortunately, this means that during the day my head can be left in a fog. I have used the Parasym to combat this brain fog. It is an effective tool without the side effects of adding another medication into the mix.”
Who is for it?
Nurosym targets the vagus nerve via the ear. It holds promise for those with brain fog and other persistent conditions like depression, particularly in instances where traditional treatments have failed.
Additionally, Nurosym is suitable for those seeking less invasive options or who have conditions limiting medication use, making neuromodulation an attractive option. Neuromodulation can help restore autonomic nervous function and reduce not only brain fog symptoms but also other brain fog-associated diseases.
Protocol - How to Use
Based on research findings and patient feedback, it is recommended to conduct Nurosym sessions for treating brain fog for at least 30 minutes twice daily, typically in the morning and before bedtime to improve vagal tone. As reducing inflammatory processes in the body requires a longer time of therapy.
The Nurosym device settings should be personalised for each patient's response, starting at lower intensities and the tingling point that indicates the point of stimulation of the vagus nerve. Most patients may begin to notice improvement within 5 days. However, the best results are typically achieved by 4 weeks of therapy.
How often
Nurosym is recommended for use twice daily based on clinical research and patient feedback. This regimen ensures optimal energy balancing and nervous system calming.
How long
Users should allocate 30 minutes in the morning and 60 minutes before sleep for Nurosym therapy sessions. Consistency in application is key to achieving desired results.
Results
Positive outcomes from Nurosym therapy may become noticeable within a relatively short timeframe. Many individuals report improvements within days of starting treatment.


