Depression and the Vagus Nerve
Depression is often characterised by a state of increased sympathetic “fight-or-flight” and decreased parasympathetic “rest-and-digest” activation within the autonomic nervous system. The vagus nerve, a vital part of the parasympathetic system, facilitates communication between the brain, heart, and digestive system. This function is crucial for maintaining emotional balance and mental well-being, which helps in preventing or mitigating the symptoms of depression. The connection between depression and the vagus nerve shapes our mental health:
Impact of Prolonged Stress on Depression
Continuous exposure to stressors, including challenging life events and traumatic experiences and trigger reminders of the latters can chronically activate the sympathetic nervous system, potentially leading to prolonged stress symptoms and vagus nerve dysfunction. Without sufficient periods of rest and recovery, the combination of ongoing stress and related vagus nerve dysfunction may induce symptoms of depression¹.
Vagus Nerve and Neurotransmitter Balance
The vagus nerve has a profound impact on both cognitive function and mood, largely due to its role in the gut-brain axis. When disruptions occur in this axis, it can lead to neurotransmitter deficiency in the brain, resulting in a decline in mood. In depression, decreased serotonin levels can further complicate symptoms².
Brain Function Changes
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) reduction was observed in patients with depression. Chronic stress and depression impact the cholinergic system, modulated by signals dependent on proper vagal function. The cholinergic system, centred around acetylcholine, is vulnerable to fluctuations in BDNF levels, influencing memory and attention. Alterations in the cholinergic system contribute to structural and functional changes in specific brain areas, including the hippocampus. The hippocampus, responsible for regulating memories and emotions, may undergo atrophy — a reduction in size and function³.
Vagal Tone Reduction in Depression
Vagal tone reduction is observed in cases of prolonged depression. This decrease can contribute to dysautonomia, associated with various physiological markers, such as heart rate variability. Importantly, these changes have the potential to worsen symptoms of depression⁴.
- Bonaz B., Sinniger V. and Pellissier S. (2017). The Vagus Nerve in the Neuro-Immune Axis: Implications in the Pathology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Front. Immunol. 8:1452.
- Mörkl S., Butler M. I., and Wagner-Skacel J. (2023). Gut-brain-crosstalk- the vagus nerve and the microbiota-gut-brain axis in depression. A narrative review, Journal of Affective Disorders Reports: 13, 2666-9153.
- Wan R., Weigand L.A., et al. (2014). Evidence that BDNF regulates heart rate by a mechanism involving increased brainstem parasympathetic neuron excitability. J Neurochem. 129(4):573-80.
- Sheena S., Shikha J., et al.. Depression affects autonomic system of the body? Yes, it does! Journal of Education and Health Promotion 9(1): 217
Nurosym induces the activation of the vagus nerve through targeted auricular neuromodulation. This precise message upregulates parasympathetic activity, momentarily suppressing the stress response. By enhancing relaxation and exerting a calming effect on the body, Nurosym contributes to both an acute and long-term improvement in mood.
By enhancing the functionality of the vagus nerve, Nurosym device is hypothesised to boost serotonin production, which is crucial for proper communication within the brain-gut axis network — a key factor in cognitive health and mood regulation. By reducing gut inflammation, optimising nutrient absorption, and maintaining the gut barrier's integrity, the vagal neuromodulation can help alleviate depression symptoms at the gut level, a primary site of serotonin synthesis.
The hippocampus is frequently the earliest and most severely impacted structure in various neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression. Nurosym enhances the production of BDNF, a key biomarker of neuroplasticity. Increased neuroplasticity within the hippocampus makes the hippocampus highly responsive to modulatory stimuli. This showed positive correlation with improvements in depressive symptoms and enhanced connectivity between different brain regions.
Nurosym provides a proprietary neuromodulation that enhances vagus nerve activity. By increasing vagal tone, Nurosym enhances heart rate variability (HRV). HRV is a marker of cardiac and autonomic health, and it tends to decline with age. Higher HRV and physical activity have been correlated with the decline of depression symptoms.
Nurosym Research-Based Evidence
74% of Nurosym patients reported more positive thinking and less stress about the future in as little as 10 days.
In clinical Nurosym trials patients after 10 days of neuromodulation therapy experienced on average 43% improved mood according to the Beck Depression Scale.
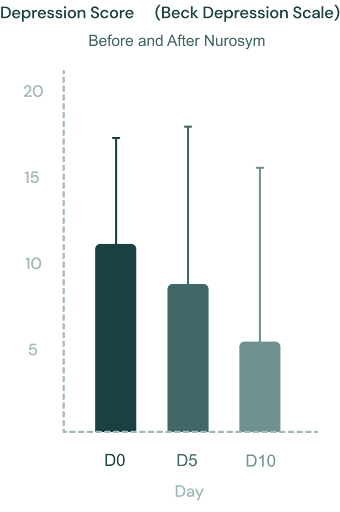
Fig. Evolution of the Beck depression scale scores during treatment (day 0, day 5 and day 10). The individual values and the median are shown. Non parametric Friedman statistics for paired comparisons were used and followed by post-hoc Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. (Parasym clinical trial, 2021)
Inflammation may correlate with depression, with studies showing changes in inflammatory markers over time are related to antidepressant response. In clinical trials after Nurosym neuromodulation, patients experienced up to 78% decrease in inflammatory cytokines level (IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α).
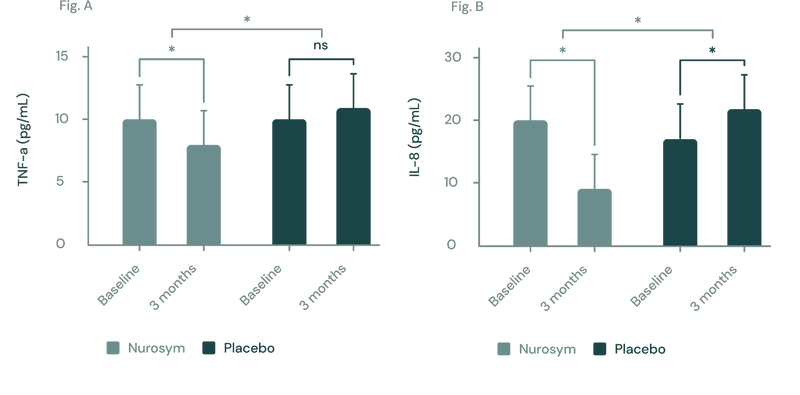
(Figure A, B) In a three-month study employing the Nurosym device for heart failure patients, notable improvements (*P<0.05) were noted in inflammatory biomarkers: (A) Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF)‐α exhibited a ~23% reduction, while (B) Interleukin (IL)‐8 showed a marked ~61.3% reduction. The investigation specifically targeted participants with elevated baseline inflammation levels (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2022).
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) can be used as an indication of clinical state in depression. Nurosym improved HRV by 61%with better effects in people with a poorer baseline HRV ratio.
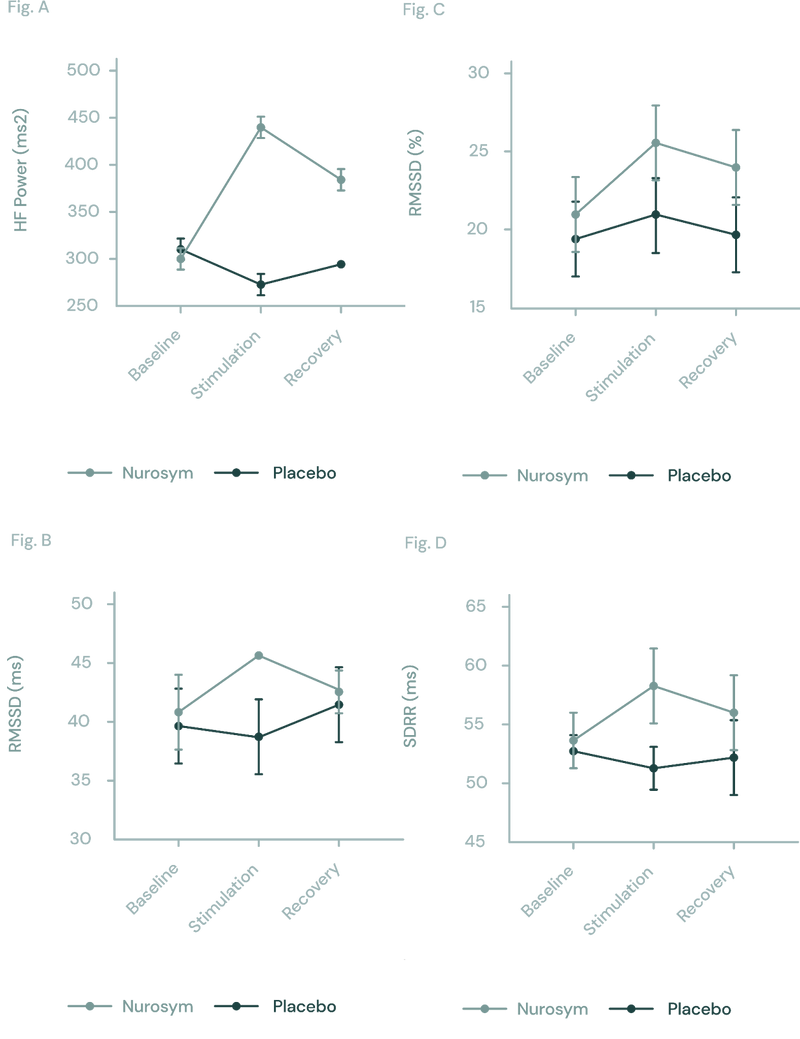
(Figure A, B, C, D) In the autonomic function response, Nurosym Neuromodulation positively changed all HRV parameters (A: HF, B: RMSSD, C: pRR50, D: SDRR) (Parasym Clinical Trial, 2022).
Studies have demonstrated that pre-existing conditions such as anxiety can exacerbate depression symptoms. The Nurosym research trial confirmed a strong connection between the presence of both anxiety and depression symptoms. The trial observed a 35% reduction in anxiety symptoms, which was associated with significant improvements in depression.
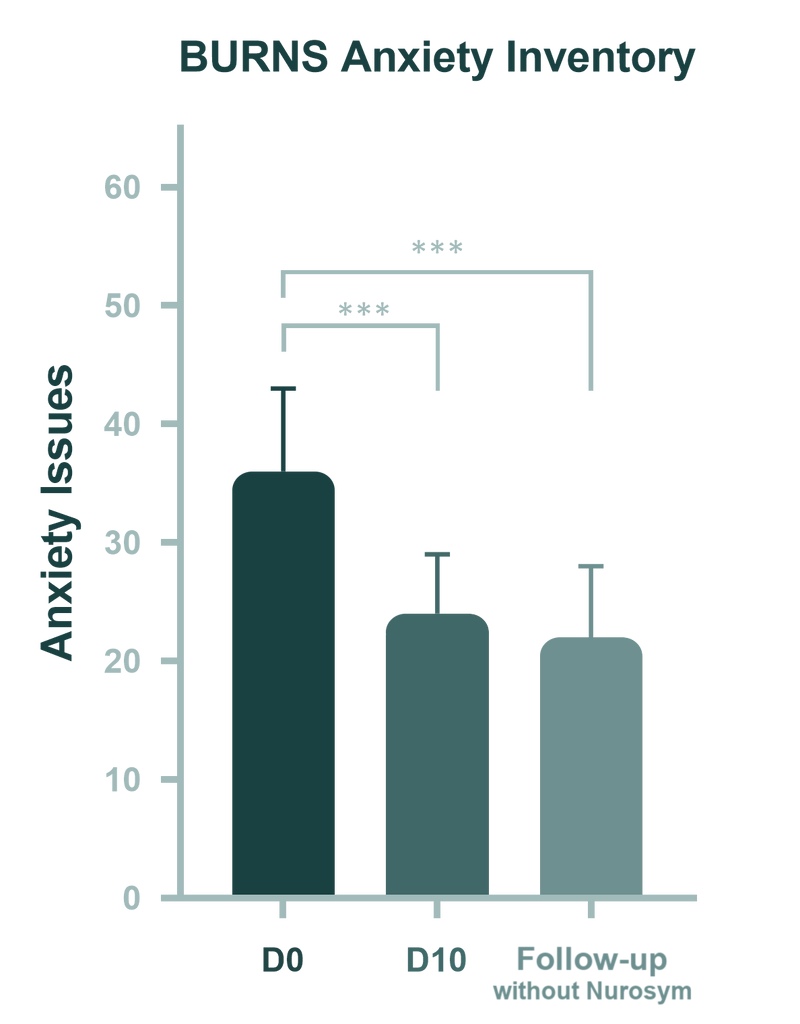
The figure illustrates changes in anxiety across three timepoints: pre-intervention (D0: Day 0), post-intervention (D10: Day 10), and 1-month follow-up after accomplished treatment. Boxplots are used for nonparametric data, while column graphs depict parametric data. Error bars represent the standard error. Significant level is indicated as ***p < 0.001 (Parasym Clinical Trial, 2024).
Doctors about Nurosym
Patients about Nurosym
“I find the ability to relax so much easier and more outgoing. The negative thoughts that I had repetitively each day have been reduced.”
Nick
“It is an effective tool without the side effects of adding another medication into the mix.”
Who is for it?
Nurosym is most suitable for individuals resistant to traditional drug treatments for depression or those exploring alternatives with less invasive, non-pharmacological methods. Vagus nerve stimulations is FDA-approved treatment for drug-resistant depression.
Considering comorbidities that may limit the use of certain medications, neuromodulation therapy becomes a valuable medical approach. Neuromodulation was confirmed as a safer approach compared to the side effects associated with antidepressant drugs.
Research and doctors often suggest neuromodulation, for individuals dealing with mild to moderate depression without need of additional medicines. Therapy can be employed in patients with depression experiencing dysthymia, cyclothymia, somatic illness,, as well as adaptive disorders.
Protocol - How to Use
Based on research findings and patient feedback, it is recommended to use Nurosym for 30 minutes both in the morning and before sleep for the treatment of depression. It may be beneficial to administer neuromodulation in the morning when cortisol levels are naturally higher, as this may enhance the antidepressant effects of the treatment and improve stress resilience. Some patients notice improvement within a short time frame, as early as 5 days of treatment.
How often
Nurosym is recommended for use twice daily based on clinical research and patient feedback. This regimen ensures optimal energy balancing and nervous system calming.
How long
Users should allocate 30 minutes in the morning and 60 minutes before sleep for Nurosym therapy sessions. Consistency in application is key to achieving desired results.
Results
Positive outcomes from Nurosym therapy may become noticeable within a relatively short timeframe. Many individuals report improvements within days of starting treatment.


