Vagus Nerve and Its Role in Sports Performance & Recovery
Impairment of the vagus nerve can have significant implications for athletic performance and muscle recovery, leading to issues such as reduced heart function and delayed tissue recovery following injuries. This is especially relevant due to its extensive involvement in the parasympathetic “rest and digest” nervous system, which supplies efferent fibres to most organs. Dysfunction of the vagus nerve can occur due to various factors, including chronic stress, toxins, intense physical training, injuries, or infections. Here's how vagus nerve dysfunction can affect these areas:
Heart Rate Variability Reduction
Impairment of the vagus nerve can lead to decreased parasympathetic activity, as can be observed through a reduction in heart rate variability (HRV). When the function of the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is compromised, the activity of neurons projecting to vagal efferent nuclei is diminished. This results in weakened vagal control over cardiac activity. A decrease in HRV is often indicative of a reduced body's capacity for effective relaxation and recovery. Dysfunction in the controlling heart rate can disrupt the balance between energy expenditure and recovery, crucial for optimal athletic performance and increase fatigue, stress and anxiety¹.
Reduced Stress Recovery
The overactivity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis can lead to excessive stress, posing a risk for vagus nerve dysfunction in athletes. Prolonged activation of the stress response system, coupled with high cortisol levels, can lead to an imbalance in the HPA axis. While cortisol is essential for stress resilience, excessive levels can impair the body's natural stress management mechanisms. The vagus nerve plays a critical role in modulating this response, and its underactivity can hinder an athlete's ability to effectively manage and recover from stress. Consequently, this imbalance can lead to chronic anxiety and a decline in athletic performance, highlighting the importance of maintaining vagal nerve function for optimal stress management and recovery².
Increased Inflammation
Age-related and infection-induced increases in inflammation may impair vagal function in athletes. The vagus nerve, through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP), plays a key role in regulating inflammation, which is important in muscle regeneration. When the vagus nerve is damaged, there is an increased risk of systemic inflammation. This condition can lead to increased fatigue and prolonged recovery time, significantly impacting the athlete's ability to heal from injuries and effectively regenerate muscle tissue³.
Reduced Sleep Quality
The quality of sleep, essential for sports recovery, is influenced by the vagus nerve, which helps regulate the balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. Stress and eating habits, such as increased meal frequency, can disrupt this balance, leading to impaired vagal tone and, consequently, poor sleep quality. This has a direct impact on regeneration during the deep sleep phase and sports performance, even its mental aspect. Impairment of the vagus nerve may also affect brain structures involved in sleep regulation, including the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem. This nucleus processes sleep-related sensory information such as catecholamines and circadian control, which helps maintain an exercise routine¹'³.
Reduced Functionality
The vagus nerve plays a significant role in pain perception and modulation, directly impacting muscle regeneration, especially in athletes. When the vagus nerve is impaired, it can lead to an increased sensitivity to pain. A decrease in vagal activity can therefore disrupt normal pain perception, leading to increased sensitivity to both physical sensations and emotional responses to pain. This heightened pain perception can significantly obstruct an athlete's training routines and hinder effective recovery processes following intense physical activity or injury⁴.
Impaired Gastrointestinal Functioning
The vagus nerve, as an integral part of the neuroendocrine-immune axis, is controlling gastrointestinal motility, pancreatic endocrine and exocrine secretion, hepatic glucose production, and other visceral functions. Disruption in vagus nerve function can lead to increased inflammatory responses in the gut, which might affect an athlete's performance. This disruption can cause issues like altered intestinal motility and changes in digestive secretions, leading to gastrointestinal complications. For athletes, these problems can result in symptoms like fatigue, elevated stress, and mood changes, along with potential cardiovascular irregularities⁵.
- Karemaker J.M. (2022). The multibranched nerve: vagal function beyond heart rate variability. Biological Psychology 172, 108378, 0301-0511.
- Herman J. P., McKlveen J. M., et al. (2016). Regulation of the Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenocortical Stress Response. Comprehensive Physiology, 603–621.
- Kim H., Jung H.R., et al.. (2022). Autonomic Dysfunction in Sleep Disorders: From Neurobiological Basis to Potential Therapeutic Approaches. J Clin Neurol. 18, 2, 140-151.
- Gourine A.V., & Ackland G.L. (2019). Cardiac Vagus and Exercise. Physiology, 1, 34(1), 71-80.
- Breit S., Kupferberg A., et al. (2018). Vagus Nerve as Modulator of the Brain–Gut Axis in Psychiatric and Inflammatory Disorders. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9.
Nurosym's activation of the parasympathetic nervous system via the vagus nerve, as indicated by increased heart rate variability (HRV), plays a key role in an athlete's recovery and performance. Neuromodulation effectively increases HRV, showing a lasting effect after stimulation and demonstrating improved vagal tone. By acting on the parasympathetic system, Nurosym promotes relaxation and regeneration, which are necessary after physical exercise. Consequently, athletes using Nurosym may experience improved performance, better stress management, and more effective inflammation control, all of which are key to maintaining peak physical condition and optimising athletic performance.
Nurosym enhances vagus nerve function, which has been proven to modulate the overactivity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. By improving vagal tone, Nurosym contributes to the rebalancing of neurotransmitter levels and enhances cellular stress resilience. This leads to more effective stress management and a reduction in chronic anxiety, both of which are crucial for maintaining optimal athletic performance. The increase in physiological signalling is particularly important for athletes, aiding in regeneration and mitigating the bodily impacts of stress. These benefits are especially significant in high-performance sports, where managing stress and optimising recovery are key to success.
Research on Nurosym has demonstrated its potential in reducing levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, which is crucial in managing systemic inflammation and enhancing the body's regeneration processes. This is achieved through the activation of the vagus nerve's efferent branch, a key component of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. By reducing systemic inflammation, Nurosym may not only alleviate fatigue but also improve gastrointestinal functions. For athletes, this implies enhanced recovery post-exercise, optimal nutrient absorption, and improved physical resilience.
By modulating the activity of the vagus nerve, Nurosym can contribute to the normalisation of sleep patterns. Its autonomic improvement effect on the nervous system has been shown to enhance sleep quality, thereby enhancing overall health and energy levels. For sports athletes, improved sleep quality directly translates to better physical recovery and enhanced performance during training and competitions. Additionally, the restorative sleep facilitated by Nurosym can lead to improved mental clarity and focus, crucial for athletes in high-pressure and strategic aspects of their sports.
Nurosym showed a significant improvement in physiological parameters, including muscle strength and blood oxygen saturation. Stimulation of the vagus nerve may play a role in muscle regeneration, promoting increased tissue oxygenation and improved blood circulation, as indicated by Nurosym research. Furthermore, the vagus nerve, through the modulation of inflammatory responses via the neural reflex cholinergic mechanism, can facilitate tissue and muscle repair both during training and injury. Additionally, it may normalise the perception of pain, potentially aiding in the maintenance of a training schedule and enhancing pain tolerance.
Nurosym, by activating the vagus nerve, optimises the functioning of the digestive tract and pancreas, thereby improving vagal tone. This nerve, which is an integral part of the central nervous system (CNS), plays an important role in the parasympathetic innervation of the gastrointestinal system. By enhancing motor skills and enzyme secretion, athletes can better cope with absorbing large amounts of protein and calories for improved muscle regeneration. Nurosym may facilitate more efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients, potentially reducing fatigue and stress. Nurosym also affects vagal pathways and may help alleviate symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
Nurosym Research-Based Evidence
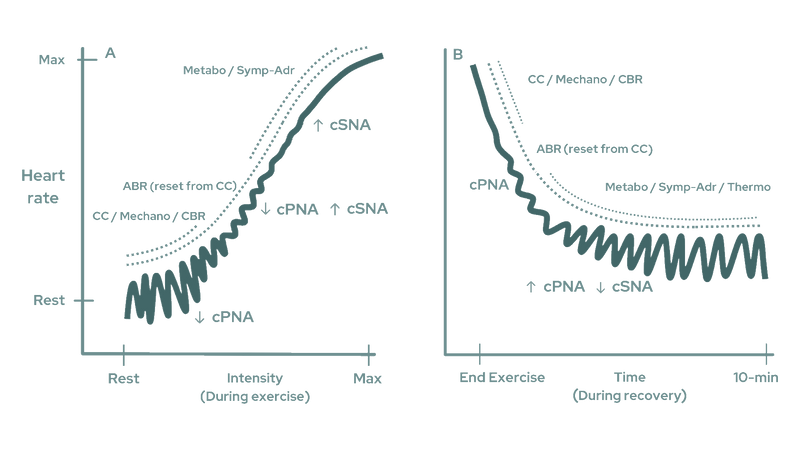
After exercise, the vagus nerve's activity increases significantly, promoting a rapid decrease in heart rate and facilitating recovery. Nurosym, especially after aerobic exercise, enhances vagal tone, meaning the vagus nerve becomes more effective in lowering the heart rate both at rest and during recovery, contributing to overall cardiovascular efficiency and health.
92% of Nurosym patients after 3 months of regular treatment observe positive outcomes in heart rate variability (HRV), which serves as an indicator of an enhanced parasympathetic nervous system response, potentially contributing to better recovery, reduced muscle fatigue, and optimised readiness for physical activity.
In the Nurosym research, the neuromodulation group was associated with improved heart rate variability (HRV), including a substantial 61% increase in measures of cardiac vagal activity (HF parameter), along with significant improvements in other parameters (18% RMSSD, 25% pRR50, 14% SDRR), when compared to the placebo group.
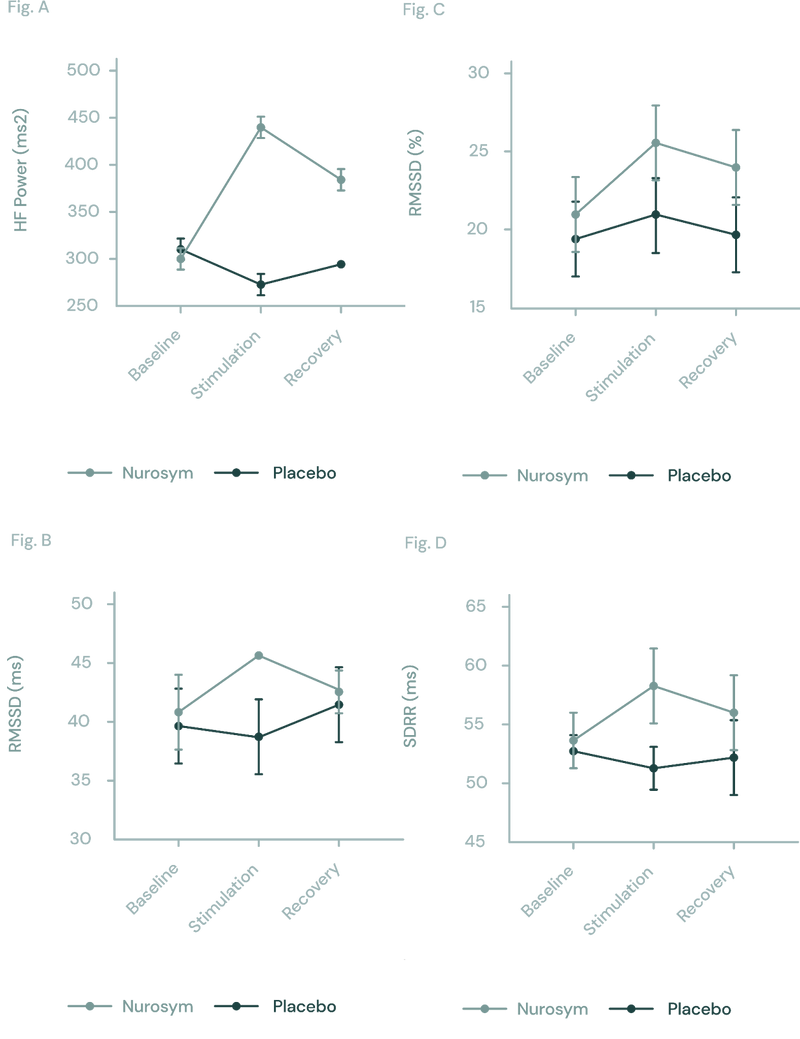
Fig (A, B, C D). The response of autonomic function measured by HRV in Nurosym or Placebo conditions over time: (A) HF, (B) RMSSD, (C) pRR50, (D) SDRR. With Nurosym, the measurements of HF, RMSSD, PRR50 and SDRR were significantly higher than those in Placebo (Parasym Clinical Trial, 2022).
These findings suggest a notable shift towards the parasympathetic side, indicating a more pronounced relaxation response, which can have positive implications after training and further enhance motor functionality.
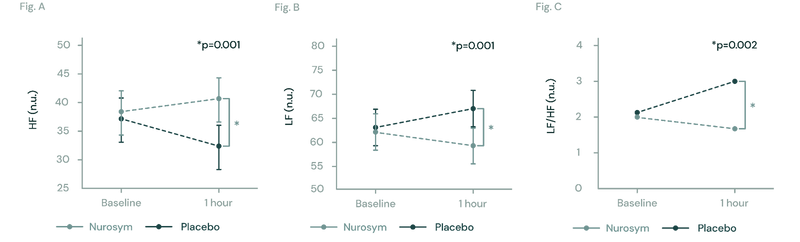
Fig (A, B, C). The figures illustrate changes in heart rate variability (HRV) during Nurosym neuromodulation. In Figure (A), High Frequency HRV significantly increases (*p=0.001). In Figure (B), Low Frequency HRV significantly decreases (*P=0.001). Figure (C) demonstrates that the ratio of LF to HF is significantly decreased (*p=0.002) (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2018).
Following a single day of Nurosym therapy, a 50% augmentation in blood vessel flow-mediated dilatation (positive effect on peripheral microcirculation) was observed. This indicates a promotion of healthy vascular function and an enhancement in nutrient supply to the tissues.
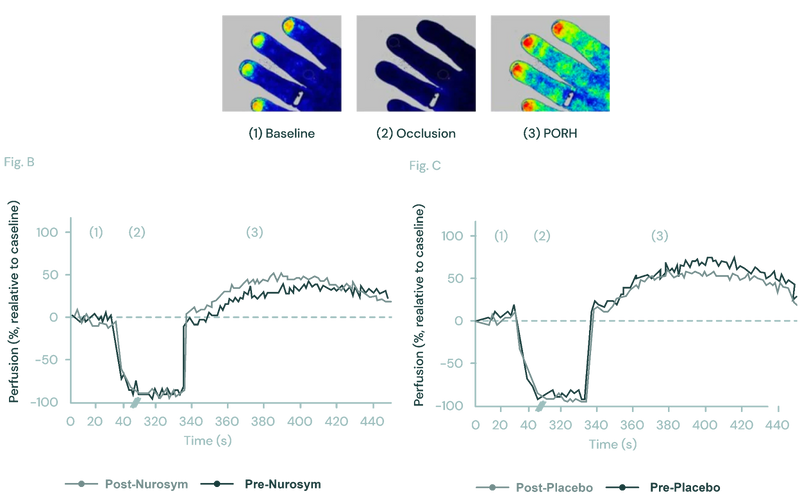
(Fig). Effect of the Nurosym neuromodulation on peripheral microcirculation using laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI). In the LSCI recordings of the left hand dorsum, (1) pseudo colour images showed baseline, (2) occlusion, and (3) post-occlusive reactive hyperemia (PORH) phase. Blue indicated lower, while red indicated higher perfusion rates. Comparing blood perfusion changes over the nail bed area before and after Nurosym neuromodulation (B) and Placebo stimulation (C), significantly higher perfusion rates were observed after Nurosym (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2020).
Atrial fibrillation (AF) commonly occurs during high-intensity exercise. In the Nurosym study, individuals diagnosed with atrial fibrillation (AF) witnessed a significant 85% reduction in AF burden measures after undergoing Nurosym treatment for a duration of 6 months, as opposed to the placebo control group.
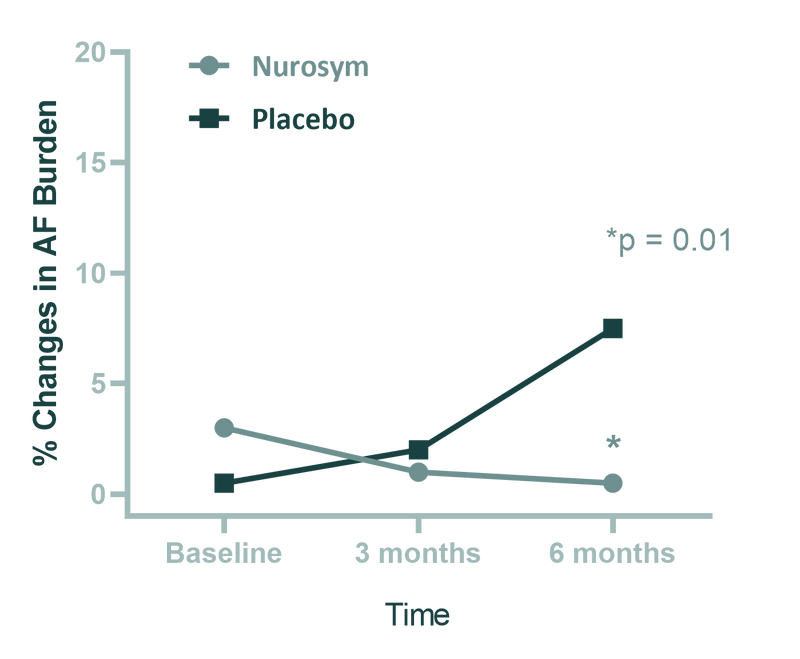
Fig. Comparison of atrial fibrillation (AF) burden between the 2 groups (Nurosym neuromodulation and Placebo stimulation) after 6 months treatment. Patients undergoing Nurosym treatment exhibit higher baseline measurements, indicating a greater improvement. The data are presented as median and interquartile range. The p value is based on a comparison of median AF burden levels at the 6-month time point after adjusting for baseline measures. (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2020).
After 3 months of Nurosym treatment, a decrease in the deformation of the heart muscle (higher GLS) of ~19% was observed compared to the control group. This improvement was associated with a reduction in cardiovascular disease risk factors, which is particularly important in professional athletes when there is an increased risk of heart deformation, especially among bodybuilders.
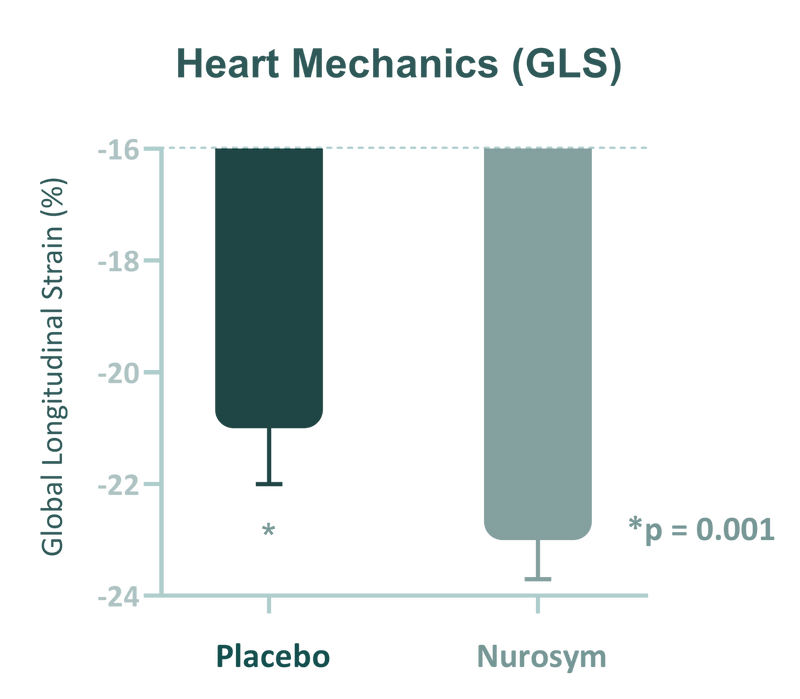
Fig. Changes in global longitudinal strain (GLS). Nurosym neuromodulation indicates significant improvement in GLS parameter, compared to Placebo (*P<0.05) (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2018).
Another finding from Nurosym's research indicates a significant, up to 78% reduction in inflammation, visible in reduced levels of cytokines such as IL-8, IL-6 and TNF-α. For athletes, it is associated with lower oxidative stress, improved heart, digestive, intestinal and hormonal function.
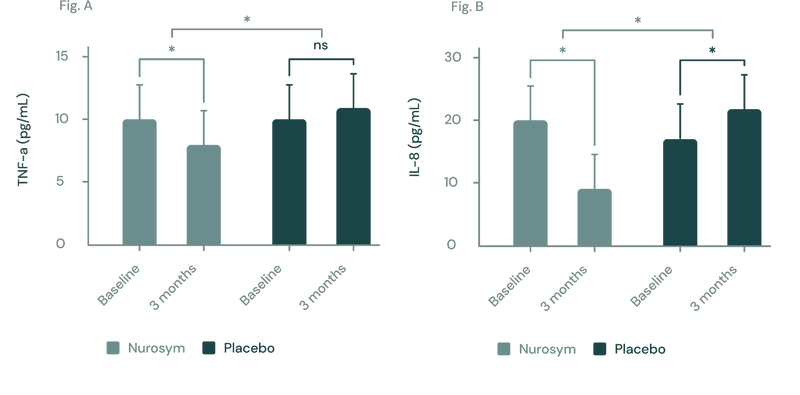
(Figure A, B) In a three-month study employing the Nurosym device for heart failure patients, notable improvements (*P<0.05) were noted in inflammatory biomarkers: (A) Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)‐α exhibited a ~23% reduction, while (B) Interleukin (IL)‐8 showed a marked ~61.3% reduction. The investigation specifically targeted participants with elevated baseline inflammation levels (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2022).
Nurosym neuromodulation helps sustain lower neuropeptide Y (NPY) levels by about 38% in atrial fibrillation progression, compared to the Placebo group. In athletes, this reduction can further improve endurance, accelerate recovery, and optimise performance.
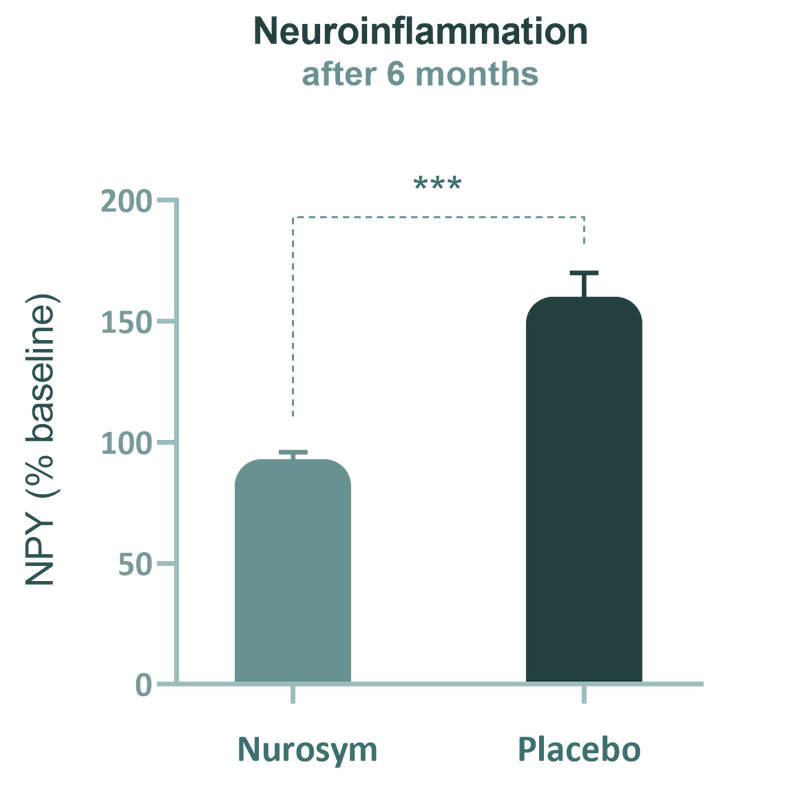
(Fig). Significant reduction in circulating neuropeptide Y (NPY) concentrations was observed after 6 months of Nurosym treatment. NPY is associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) progression and higher cardiovascular risk (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2020).
48% fatigue improvement was evident in the research findings, reflecting positive outcomes in athletes' routines.
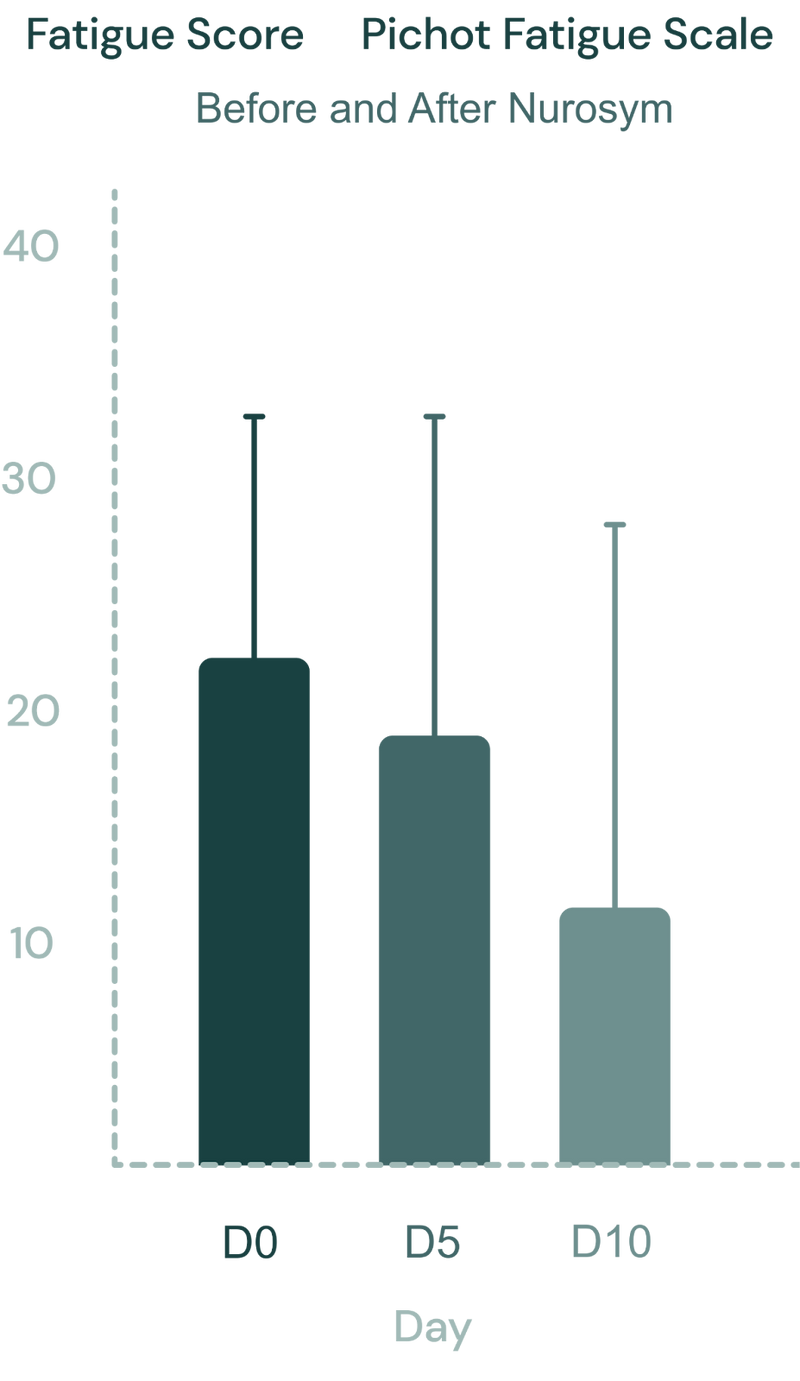
Fig. The Pichot fatigue scale scores during Nurosym therapy (D0: day 0, D5: day 5 and D10: day 10). Significant improvement in fatigue scores after Nurosym treatment was observed (D0 vs. D10, p<0.0001). (Parasym clinical trial, 2021)
Nurosym has been shown to enhance hand strength by 7% after 10 days (in non-training individuals, ruling out exercise-driven effect), a factor that holds significant implications for the performance of muscles, tendons, and ligaments, as well as the control of movements.
Nurosym has demonstrated a 1% increase in oxygen saturation among half of the participants (in non-training individuals, eliminating exercise-driven effects). This improvement enhances tissue oxygenation, body performance, and muscle regeneration.
Doctors about Nurosym
Patients about Nurosym
Alex Katchur
“I originally became interested in Nurosym [formerly Parasym] with the primary goal to improve sleep consistency and boost recovery. However, I soon realised that daily use reduced my stress levels. My brain health has significantly improved. The benefits have leaked into all parts of life: focused work, attentive personal life, sports,etc. Also this device is a must have for parents with young children. A few minutes of parasym helps falling back to sleep and getting quality sleep. Great product.”
“I'm a long COVID sufferer, and I started using Nurosym [formerly Parasym] because of a lot of neurological issues I developed because of the long COVID. For instance, I had a lot of muscle spasms, and I was also overly sensitive to external stimuli. So some days I couldn't do anything but just lay down with noise cancelling headphones and dim the light. And that changed after I started using Nurosym on a daily basis.”
Who is for it?
People involved in a variety of physical activities, from Olympic athletes to martial arts and bodybuilding enthusiasts, can greatly benefit from Nurosym therapy. Nurosym contributes to restoring the balance of the autonomic nervous system, relieving inflammation for better muscle recovery, optimising breathing patterns to prevent asthma and improve exercise quality, and enhancing circulation to revitalise tissues. Another advantage is the relief of neurological symptoms related to the digestive system. The positive effects of Nurosym, including improved oxygen and nutrient delivery, optimisation of cardiovascular health, regulation of blood pressure, and the potential for increased performance, provide benefits to athletes who seek improvements in these areas.
Protocol - How to Use
In the context of sports performance, the inclusion of Nurosym after training sessions may prove beneficial due to its ability to activate the parasympathetic nervous system and stimulate muscle metaboreceptors. Using Nurosym after training may contribute to faster regeneration, reduced inflammation, and stress reduction. Moreover, it is worth using Nurosym for at least 15 minutes after meals, as it can positively impact the digestive capacity of protein and enhance the absorption of nutrients from food.
For athletes concerned with heart health, potential benefits of Nurosym include reduced inflammation and improved cardiovascular function. It is worth noting that these positive results may become noticeable after use for a period of three months.
How often
Nurosym is recommended for use twice daily based on clinical research and patient feedback. This regimen ensures optimal energy balancing and nervous system calming.
How long
Users should allocate 30 minutes in the morning and 60 minutes before sleep for Nurosym therapy sessions. Consistency in application is key to achieving desired results.
Results
Positive outcomes from Nurosym therapy may become noticeable within a relatively short timeframe. Many individuals report improvements within days of starting treatment.


