Vagus Nerve and Its Role in Anti-ageing process
Ageing is a biological process characterised by the accumulation of molecular damage in cells over time. As a consequence, cellular defects appear, leading to tissue dysfunction, increased fragility and age-related diseases. The vagus nerve in the parasympathetic part of the nervous system plays a key role in regulating immune and regenerative functions. With age, infections, and increase in cortisol levels, the function of the vagus nerve declines, which can lead to a number of syndromes, ranging from disruptions in neuronal communication between systems to problems related to inflammation, cardiovascular disease and accelerated ageing.
Heart Rate Variability Reduction
Impairment of the vagus nerve can lead to decreased parasympathetic activity, evident in reduced heart rate variability (HRV). When the function of the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is compromised, the activity of neurons projecting to vagal efferent nuclei is diminished. It results in weakened vagal control over cardiac activity. A decrease in HRV often signals a reduced capacity for effective relaxation and recovery. Dysfunction in regulating heart rate can disrupt the energy balance, crucial for longevity, potentially increasing feelings of fatigue, stress, and anxiety (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263833).
Reduced Stress Recovery
Ageing and a variety of internal and external stressors can have harmful effects on the nervous and immune systems, potentially leading to impaired vagal function. This impairment often results in an overactive hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, where the vagus nerve plays a key role in regulating the body's response to stress. When the vagus nerve is underactive, it hinders the body's ability to effectively deal with and recover from stress, which can result in oxidative stress and cell damage. These consequences, in turn, contribute to the overall ageing process, which manifests itself in physical weakness and pain (doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150015).
Inflammaging
Age- and infection-related increases inflammation, which can disrupt the vagus nerve function, leading to exaggerated fatigue and systemic inflammation. The vagus nerve, through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP), plays a key role in regulating inflammation. Chronic brain signalling, driven by an overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines and neuroexcitatory substances, can impair the vagus nerve, intensifying fatigue and other prolonged sickness symptoms associated with ageing process (doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00021, doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00616-1).
Reduced Sleep Quality
The quality of sleep, essential for sports recovery, is influenced by the vagus nerve, which helps regulate the balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. Stress and eating habits, such as increased meal frequency, can disrupt this balance, leading to impaired vagal function and, consequently, poor sleep quality. This has a direct impact on regeneration during the deep sleep phase and sports performance. Impairment of the vagus nerve may also affect brain structures involved in sleep regulation, including the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem. This nucleus processes sleep-related sensory information such as catecholamines and circadian control, which helps maintain an exercise routine (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263833, 10.1016/j.autneu.2022.102972).
Neurogenesis Impairment
Dysfunction of the vagus nerve has been associated with reduced neurogenesis, or the production of new neurons, particularly in regions critical for memory and learning such as the hippocampus. The hippocampus, responsible for regulating memories and emotions, may undergo atrophy — a reduction in size and function. This decrease in neurogenesis can hinder recall in memory, the ability to learn new information and the memory consolidation during sleep (doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2017.12.004).
Enhancing Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
Nurosym's neuromodulation approach enhances the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, resulting in an improved heart rate variability (HRV) index. This index serves as a valuable marker of cardiac and autonomic health, which typically declines with age. Elevated HRV signifies a more robust and adaptive cardiovascular system, proficient in effectively managing stressors. Furthermore, Nurosym's neuromodulation techniques have the potential to counteract excessive sympathetic activity commonly seen in conditions characterised by reduced vagal tone, contributing to the reduction of age-related decline in HRV (doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005361, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263833).
Stress Response Management
Nurosym enhances vagus nerve function, which has been proven to modulate the overactivity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. By improving vagal tone, Nurosym contributes to the rebalancing of neurotransmitter levels and enhances cellular stress resilience. This leads to more effective stress management and a reduction in chronic anxiety, both of which are crucial for maintaining optimal athletic performance. The increase in physiological signalling is particularly important for athletes, aiding in regeneration and mitigating the bodily impacts of stress. These benefits are especially significant in high-performance sports, where managing stress and optimising recovery are key to success. (doi: 10.1002/cphy.c150015, doi: 10.51956/ANNR.100011).
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Research on Nurosym has demonstrated its potential in reducing levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α), which is crucial in managing systemic inflammation and enhancing the body's regeneration processes. This is achieved through the activation of the vagus nerve's efferent branch, a key component of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. This neuromodulation offers a potential avenue for addressing inflammageing. Reduced the age-related pro-inflammatory markers, and risk of chronic diseases, disability, frailty, and early death. (doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.023582, doi: 10.1007/s10286-023-00997-z).
Sleep Regulation
By modulating the activity of the vagus nerve, Nurosym may help normalise sleep patterns and achieve the deep sleep phase, as demonstrated by a reduction in fatigue in studies. Its autonomic effects on the nervous system have been shown to improve sleep quality, which, in turn, may significantly impact cognitive function in aging individuals. Nurosym's ability to facilitate restorative sleep may play a role in improving memory consolidation and tissue rejuvenation during rest. This rejuvenation of nervous and bodily functions can have a positive effect on the ageing process, promoting mental clarity and focus (doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2022.102972).
Neuroplasticity
Nurosym has demonstrated positive effects on sequential learning and response selection processes in key brain regions, with particular emphasis on preventing age-related neurodegeneration and chronic disease. The Nurosym test confirmed this positive effect, probably resulting from neuromodulation, which enhances consolidation processes, potentially affecting activation patterns in specific brain areas (hippocampus, parahippocampus, amygdala, anterior cingulate cortex and prefrontal cortex). These changes suggest increased functionality of brain areas crucial for cognitive control, motor learning and emotional regulation, thereby contributing to improved cognitive function and the formation of new synapses. (doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01276, doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2022.114164)
Nurosym Research-Based Evidence
92% of Nurosym patients after 3 months of regular treatment observe positive outcomes in heart rate variability (HRV), which serves as an indicator of an enhanced parasympathetic nervous system response with improved capacity for relaxation and effective recovery.
In the Nurosym research, the neuromodulation group was associated with improved heart rate variability (HRV), including a substantial 61% increase in measures of cardiac vagal activity (HF parameter), along with significant improvements in other parameters (18% RMSSD, 25% pRR50, 14% SDRR), when compared to the placebo group (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263833).
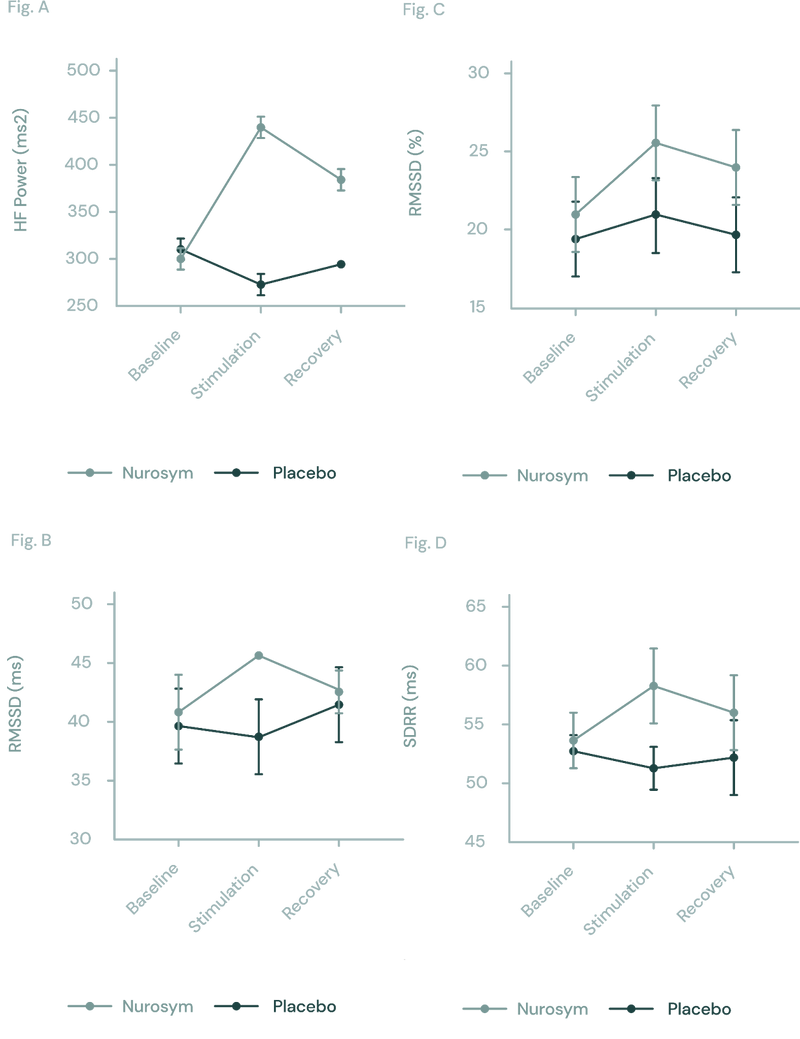
Fig (A, B, C D). The response of autonomic function measured by HRV in Nurosym or Placebo conditions over time: (A) HF, (B) RMSSD, (C) pRR50, (D) SDRR. With Nurosym, the measurements of HF, RMSSD, PRR50 and SDRR were significantly higher than those in Placebo (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263833).
Nurosym has been shown to activate central vagal projections in the brain in humans, leading to decreased sympathetic output which increases with ageing. This provides a promising correlation with longevity and anti-aging interventions (doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.023582).
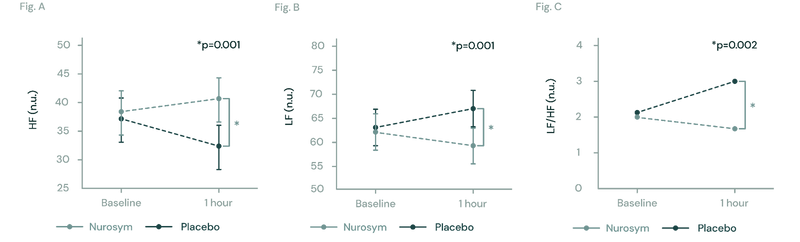
Fig (A, B, C). The figures illustrate changes in heart rate variability (HRV) during Nurosym neuromodulation. In Figure (A), High Frequency HRV significantly increases (*p=0.001). In Figure (B), Low Frequency HRV significantly decreases (*P=0.001). Figure (C) demonstrates that the ratio of LF to HF is significantly decreased (*p=0.002) (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.1007/s12265-018-9853-6).
In clinical trials, patients exhibited a 32% improvement in memory and a 26% enhancement in learning performance within 5 days of Nurosym use, suggesting potential indications of neuroplasticity that are relevant for maintaining mental health during the ageing process (doi:10.1016/j.brs.2020.10.012).
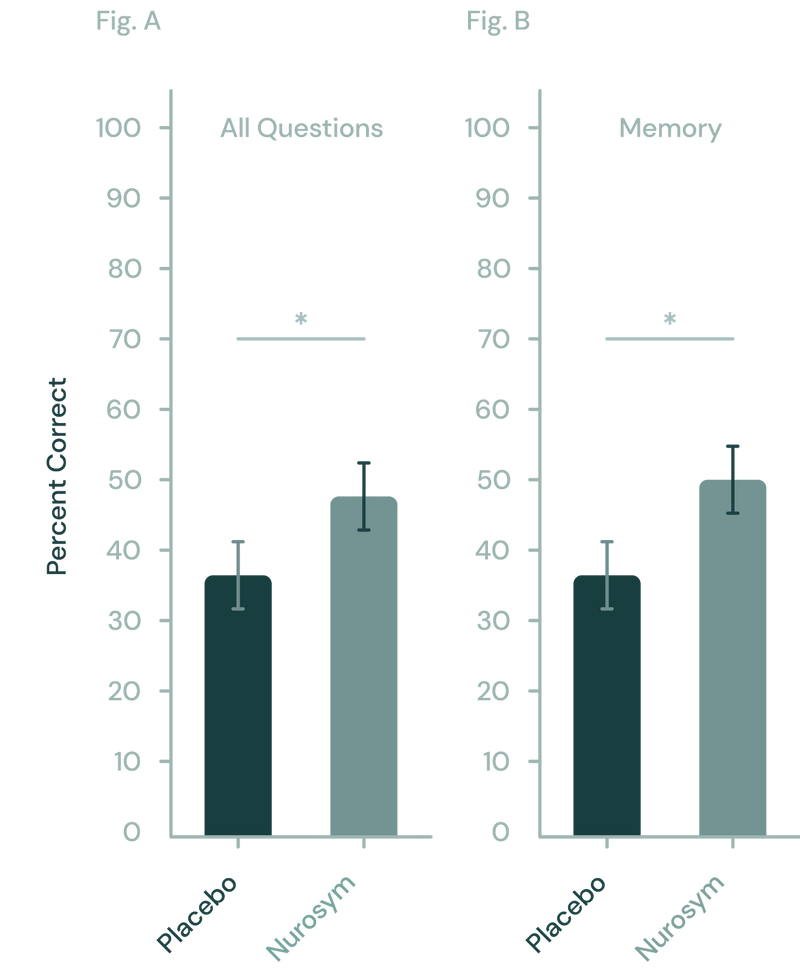
Fig (A, B). Nurosym has shown to enhance memory in learning tasks relative to a placebo. (A) Across all test questions, Nurosym's neuromodulation demonstrated a notable advantage over placebo. (B) Specifically, this improvement was largely due to the significant impact of Nurosym neuromodulation on memory-related questions (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2020.10.012).
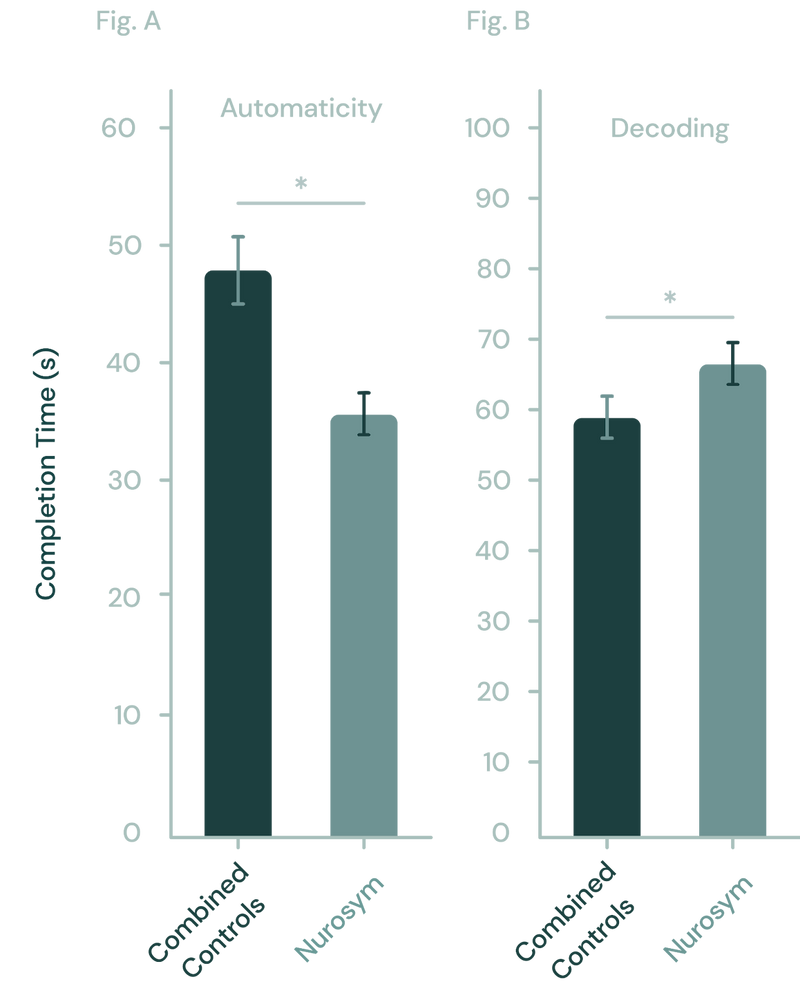
Fig (A, B). In the study, pairing Nurosym neuromodulation with training notably enhanced speed performance in the Automaticity learning task (significantly, *p<0.05), compared to placebo controls. Additionally, Nurosym neuromodulation significantly improved accuracy, as measured by the percent correct, in the Decoding learning task when compared to controls (*p < 0.05) (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2020.10.012).
Oxygen saturation decreases with the ageing process. Nurosym has demonstrated a 1% increase in oxygen saturation among half of the participants (in non-training individuals, eliminating exercise-driven effects) (doi: 10.51956/ANNR.100011).
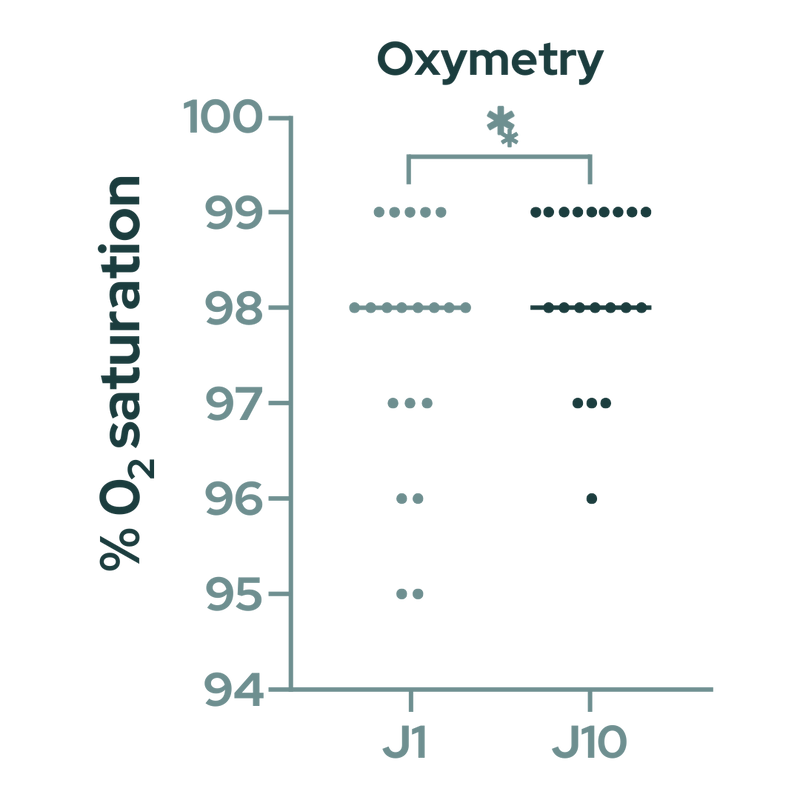
Figure 6. Evolution of arterial blood oxygen saturation before and after treatment (in % O2 arterial blood saturation). The means were compared by using paired t-test (Parasym Clinical Trial, 10.51956/ANNR.100011).
Following a single day of Nurosym therapy, a 50% augmentation in blood vessel flow-mediated dilatation (positive effect on peripheral microcirculation) was observed. This indicates a promotion of healthy vascular function and an enhancement in nutrient supply to the tissues (doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.12.017).
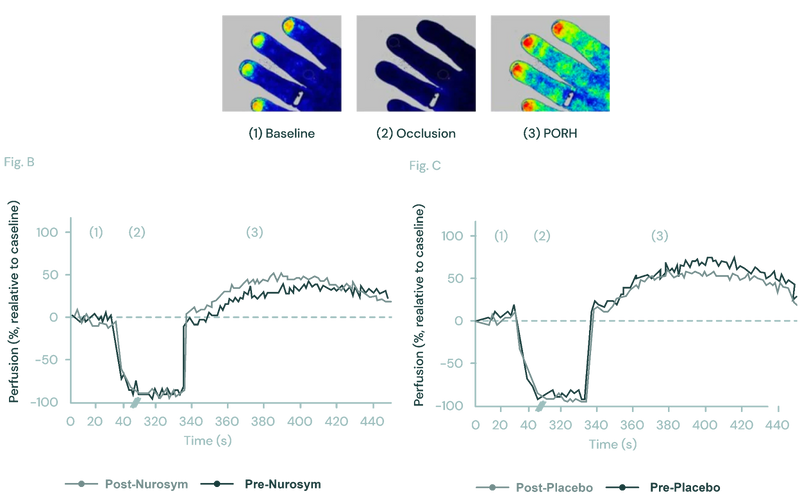
Fig. Effect of the Nurosym neuromodulation on peripheral microcirculation using laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI). In the LSCI recordings of the left hand dorsum, (1) pseudo colour images showed baseline, (2) occlusion, and (3) post-occlusive reactive hyperemia (PORH) phase. Blue indicated lower, while red indicated higher perfusion rates. Comparing blood perfusion changes over the nail bed area before and after Nurosym neuromodulation (B) and Placebo stimulation (C), significantly higher perfusion rates were observed after Nurosym (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.12.017).
Ageing is another significant risk factor for Atrial fibrillation (AF). In the Nurosym study, individuals diagnosed with atrial fibrillation (AF) witnessed a significant 85% reduction in AF burden measures after undergoing Nurosym treatment for a duration of 6 months, as opposed to the placebo control group. (doi:10.1016/j.jacep.2019.11.008,10.1161/JAHA.120.020865).
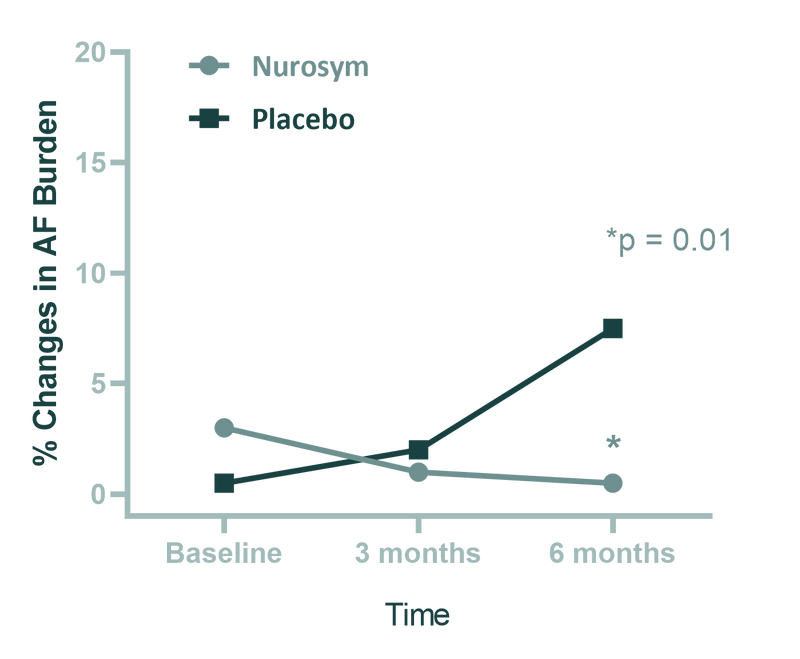
Fig. Comparison of atrial fibrillation (AF) burden between the 2 groups (Nurosym neuromodulation and Placebo stimulation) after 6 months treatment. Patients undergoing Nurosym treatment exhibit higher baseline measurements, indicating a greater improvement. The data are presented as median and interquartile range. The p value is based on a comparison of median AF burden levels at the 6-month time point after adjusting for baseline measures. (Parasym Clinical Trials, TREAT AF).
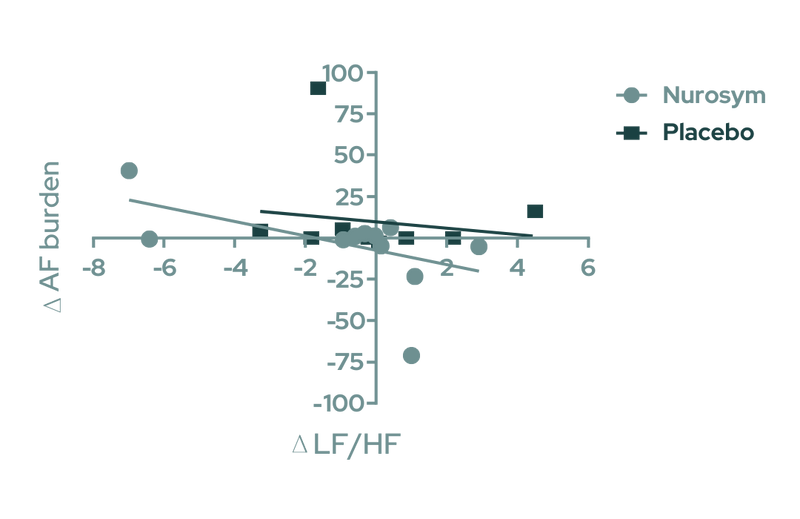
Fig. Association of Heart Rate Variability With the Change in AF Burden. Linear regression of the change in atrial fibrillation (AF) burden at follow-up (Δ AF burden) as a function of the respective change in low frequency to high frequency ratio (Δ LF/HF) in the Nurosym neuromodulation and Placebo control groups.( Parasym Clinical Trials, doi:TREAT AF).
Ageing is associated with increased inflammatory activity in the blood, including increased circulating levels of TNF-α. Nurosym's research indicates a significant, up to 78% reduction in inflammation, visible in reduced levels of cytokines such as IL-8, IL-6 and TNF-α (doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.023582).
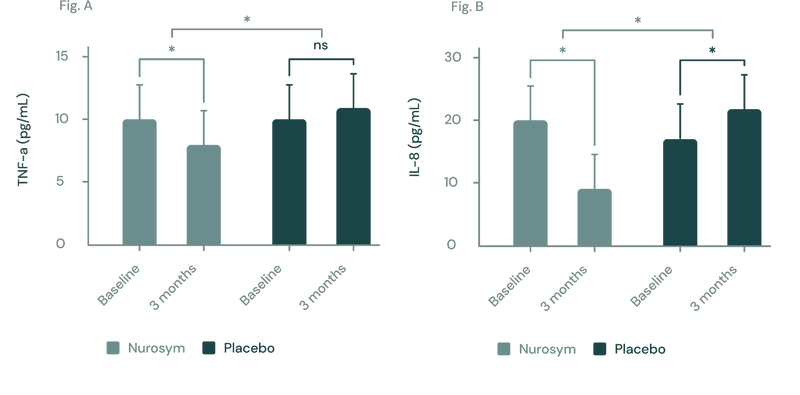
(Figure A, B) In a three-month study employing the Nurosym device for heart failure patients, notable improvements (*P<0.05) were noted in inflammatory biomarkers: (A) Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)‐α exhibited a ~23% reduction, while (B) Interleukin (IL)‐8 showed a marked ~61.3% reduction. The investigation specifically targeted participants with elevated baseline inflammation levels (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2022.10.278).
Nurosym neuromodulation helps sustain lower neuropeptide Y (NPY) levelsby 38% difference in atrial fibrillation progression, compared to the Placebo group, potentially reducing ageing process and cell damage due to reduction in neurogenic inflammation (doi: j.jacep.2020.08.025).
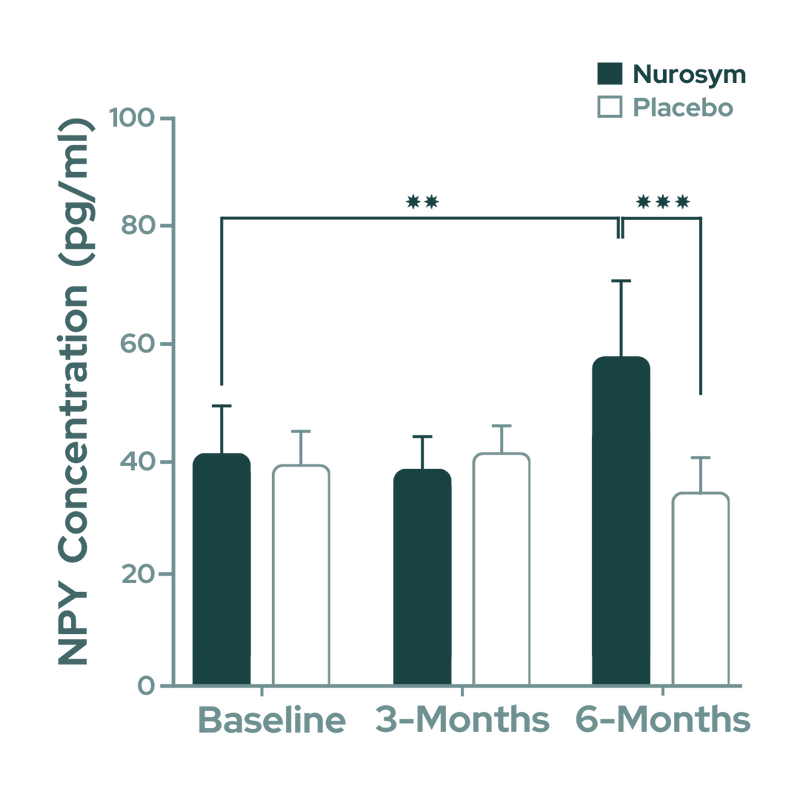
Fig. Significant reduction in circulating neuropeptide Y (NPY) concentrations was observed after 6 months of Nurosym treatment. NPY is associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) progression (Parasym Clinical Trials, doi: j.jacep.2020.08.025).
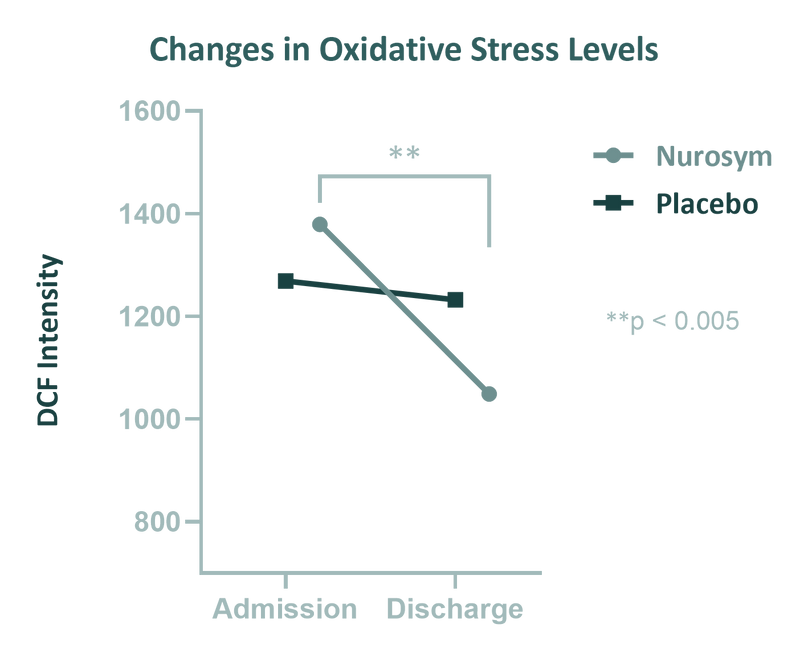
Fig. Effect of LLTS on oxidative stress. A Change in median values of DCF from admission to discharge in Nurosym group compared to control Placebo group (Parasym Clinical Trial, doi: 10.1007/s10286-023-00997-z)
The research findings revealed a significant 48% improvement in fatigue, showcasing positive outcomes in daily performance (doi: 10.51956/ANNR.100011).
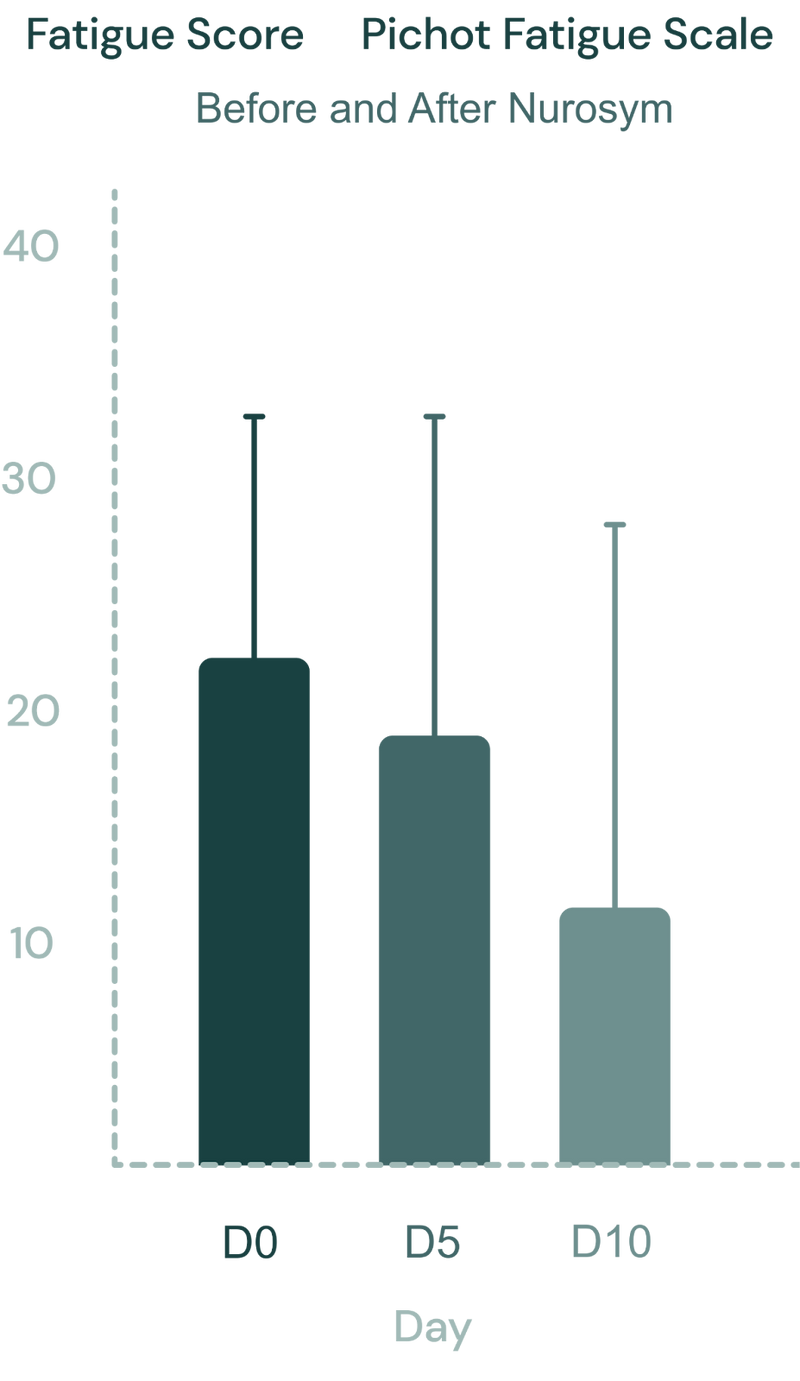
Fig. The Pichot fatigue scale scores during Nurosym therapy (D0: day 0, D5: day 5 and D10: day 10). Significant improvement in fatigue scores after Nurosym treatment was observed (D0 vs. D10, p<0.0001). (Parasym clinical trial, doi: 10.51956/ANNR.100011).
The group undergoing active neuromodulation witnessed an approximate 13% enhancement in global sleep scores, reflecting more profound sleep patterns conducive to regeneration and improved memory consolidation.
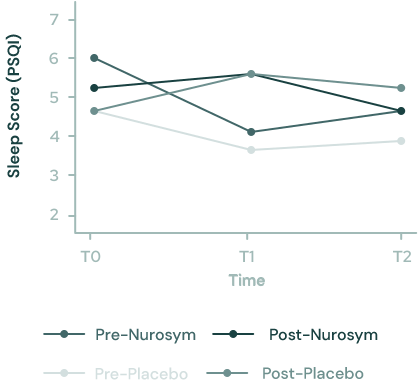
Fig. Change in global sleep scores in 4 intervention groups over the course of the study. Predicted change in global sleep scores (PSQI) with 95% confidence intervals in individuals who underwent 14 days of daily active Nurosym neuromodulation (darker grey lines) and placebo stimulation (brighter grey lines). (doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2022.102972).
Doctors about Nurosym
Patients about Nurosym
“Hello, my name is Trevor. I have been diagnosed with inflammation and told by my doctor that we don't know what is wrong, but they did want to put me on long term steroids. I started to research how I could help myself. I came across Nurosym [formerly Parasym]. And I was intrigued with the concept that the device works to harness the therapeutic mechanism of the vagus nerve. I carried out further research into the vagus nerve. To discover that the vagus nerve is responsible for regulating internal organ function such as digestion, heart rate, and respiratory rate. I decided to purchase the unit. As I started to use it, I decided to couple this with doing slow breathing exercises. And I found I felt very calm and relaxed after each session. I also found that my stress levels reduced considerably, enabling my body to go into self healing mode”.
“I'm a long COVID sufferer…I had a lot of muscle spasms, and I was also overly sensitive to external stimuli. So some days I couldn't do anything but just lay down with noise cancelling headphones and dim the light. And that changed after I started using [Nurosym; formerly Parasym] on a daily basis… So, for me, it has been an excellent treatment and I'm thankful for that.”
Tatiana
“Nurosym helped soothe the multiple inflammatory conditions I had developed after covid, such as arthritis, myocarditis, thyroiditis and brain fog. As I now feel better, I do not need to use it every day anymore, but I still incorporate it in my routine whenever I feel the need to relax and restore my nervous system and my whole body.”
Who is for it?
For individuals actively seeking to prevent age-related diseases and address cellular ageing, the regular use of Nurosym holds significant potential. Nurosym's ability to promote a feeling of calm, relaxation, and overall well-being makes it a valuable contributor to increasing daily activity and may support other anti-aging interventions. Nurosym has a positive effect on physiological functions such as intestinal motility, insulin metabolism, and even cognitive processes, making it suitable for individuals who want to maintain their autonomic system in this state or optimise its regulation.
Protocol - How to Use
Incorporating Nurosym into your daily routine, along with the tingling sensation indicating vagus nerve stimulation, can be part of a comprehensive anti-aging strategy. Based on research and patient experiences, a 15-minute intervention, especially before bedtime, has been shown to contribute to improving sleep quality. Additionally, using Nurosym after meals may positively impact gastrointestinal processes. Within three months of use, Nurosym may provide benefits such as reduced inflammation and positive effects on cognitive function, neuroplasticity, as well oxidative stress. Individual reactions may vary, and long-term use may bring lasting benefits. However, it is worth complementing these therapies with a healthy lifestyle and regular exercise.
How often
Nurosym is recommended for use twice daily based on clinical research and patient feedback. This regimen ensures optimal energy balancing and nervous system calming.
How long
Users should allocate 30 minutes in the morning and 60 minutes before sleep for Nurosym therapy sessions. Consistency in application is key to achieving desired results.
Results
Positive outcomes from Nurosym therapy may become noticeable within a relatively short timeframe. Many individuals report improvements within days of starting treatment.


