Schutz vor Demenz: Der Vagusnerv
Der Vagusnerv, ein Schlüsselelement des parasympathischen Nervensystems, reguliert nicht nur autonome Körperfunktionen, sondern spielt auch eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Modulation der Kommunikation zwischen dem Gehirn und dem Rest des Körpers. Angesichts seiner integralen Rolle in zahlreichen physiologischen Prozessen gibt es einen überzeugenden Hinweis darauf, dass eine Beeinträchtigung des Vagusnervs zur Entwicklung und zum Fortschreiten von Demenz beitragen kann, verursacht durch:
Störung der Mikrobiom-Gehirn-Achse
Der Vagusnerv spielt eine Rolle in der bidirektionalen Kommunikation zwischen dem Darm und dem Gehirn, bekannt als die Darm-Hirn-Achse. Eine Störung dieser Achse aufgrund einer Beeinträchtigung des Vagusnervs kann zu Veränderungen im Darmmikrobiom führen, mit potenziellen Konsequenzen für die Gehirngesundheit. Neue Forschungen deuten auf einen möglichen Zusammenhang zwischen der Zusammensetzung des Darmmikrobioms und dem Risiko der Entwicklung von Demenz hin, möglicherweise durch entzündliche Effekte¹.
Blut-Hirn-Schranke-Dysfunktion & Neuroinflammation
Der Vagusnerv ist an der Regulierung der Blut-Hirn-Schranke (BHS) beteiligt, deren Integrität das Gehirn vor schädlichen Substanzen schützt. Eine Dysfunktion des Vagusnervs durch entzündliche Wege und hormonelle Signale kann die Dynamik der Gehirnkommunikation verändern und potenziell schädliche Moleküle in das Gehirn eindringen lassen. Diese Störung kann zur Neuroinflammation und neuronalen Schädigung beitragen, die mit dem Fortschreiten der Demenz verbunden sind².
Beeinträchtigung der Neurogenese
Eine Beeinträchtigung des Vagusnervs ist mit einer verminderten Neurogenese, der Bildung neuer Neuronen, insbesondere in wichtigen Bereichen für Gedächtnis und Lernen wie dem Hippocampus, verbunden. Dieser Rückgang der Neurogenese kann die Schaffung neuer Gedächtnisse und die Fähigkeit, neue Informationen zu erwerben, behindern, was eine erhebliche Herausforderung im Kontext der Demenz darstellt³'⁴.
Amyloid-Beta-Akkumulation
Eine Dysfunktion des Vagusnervs kann die Ansammlung von Beta-Amyloid-Plaques im Gehirn erleichtern und den Prozess ihrer Beseitigung stören. Diese Plaques, zusammen mit Tau-Proteinen, tragen zu pathologischen Veränderungen und erhöhter Entzündung des Nervensystems bei. Ihre Ansammlung fördert und trägt zur Entwicklung von Demenz bei⁵.
- Chandra S., Sisodia S.S. & Vassar R.J. (2023). Das Darmmikrobiom bei der Alzheimer-Krankheit: Was wir wissen und was noch zu erforschen ist. Mol Neurodegeneration 18, 9.
- Knox E.G., Aburto M.R., et al. (2022) Die Blut-Hirn-Schranke im Alterungsprozess und bei Neurodegeneration. Mol Psychiatry 27, 2659–2673.
- O'Leary O.F., Ogbonnaya E.S., et al. (2018). Der Vagusnerv moduliert die BDNF-Expression und Neurogenese im Hippocampus. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 28, 2, 307-316.
- Suarez A.N., Hsu T.M., et al. (2018) Die vagale sensorische Signalübertragung des Darms reguliert die Funktion des Hippocampus über mehrstufige Signalwege. Nat Commun 9, 2181.
- Vargas-Caballero M., Warming H., et al. (2022). Vagusnervstimulation als mögliche Therapie bei früher Alzheimer-Krankheit: A Review. Sec. Brain Imaging and Stimulation 16.
Nurosym erleichtert die Übertragung von Signalen, die das Gedächtnis und die kognitive Funktion betreffen, vom Darm zum Gehirn. Studien haben die positive Wirkung von Nurosym hervorgehoben und auf seine entzündungshemmenden Effekte hingewiesen, die die Nährstoffaufnahme im Darm durch Mikrobiota verbessern. Folglich kann die Reduzierung der Entzündung zu einer verbesserten darmabgeleiteten Neurotransmitterproduktion als Reaktion auf Entzündung führen. Zusätzlich wurden ähnliche Ergebnisse in der Zeitschrift Molecular Neurodegeneration zusammengefasst, die Zusammenhänge zwischen dem Darmmikrobiom und der Pathophysiologie der Alzheimer-Krankheit (AD) identifizierten.
Nurosym, bekannt für seine entzündungshemmenden Eigenschaften und seine nachgewiesene Gedächtniswirkung, wird als potenziell vorteilhaft bei der Behandlung von Problemen im Zusammenhang mit der zerebralen Blutversorgung und der Dysfunktion der Blut-Hirn-Schranke angesehen. Die Forschung von Nurosym hat gezeigt, dass es Entzündungen im Nervensystem durch Beeinflussung von Neuropeptid Y (NPY) reduzieren kann. NPY kann die Aktivität des neurotrophen Faktors des Gehirns beeinflussen, der die Differenzierung neuer Neuronen und Synapsen unterstützt. Diese Korrelation kann die Gehirnstruktur beeinflussen, indem sie Probleme wie Barriereabbau, Gehirnschwellung und Nervenzellschäden, die mit neurogener Entzündung verbunden sind, lindert. Folglich hat Nurosym das Potenzial, kognitive und motorische Lernfunktionen zu verbessern und das Fortschreiten neuroinflammatorischer Erkrankungen zu mildern.
Das Nurosym-Gerät hat verbesserte Gedächtnisfunktionen gezeigt. Durch die Verringerung von Entzündung und oxidativem Stress kann Nurosym potenziell zum Neuroprotektion der Gehirnzellen beitragen. Es wird angenommen, dass dieser neuroprotektive Effekt die Schädigung von Nervenzellen mildert, wie durch die Entzündungsreaktion belegt. Darüber hinaus bietet die Neuromodulation-Forschung Daten, die den Schutz spezifischer Gehirnzellen im Hippocampus durch die Erhöhung des gehirnabgeleiteten neurotrophen Faktors (BDNF) unterstützen, was auf potenzielle Vorteile bei der Bewältigung von Gedächtnis- und kognitiven Herausforderungen bei Personen mit Demenz hinweist.
Es wird angenommen, dass Nurosym die grundlegende Kommunikation zwischen Gehirnzellen (Synapsen) verbessert und die kognitiven Fähigkeiten durch die Modulation von Signalen im Zusammenhang mit der Entzündungsreaktion verbessert. Nurosym hat in Forschungsstudien positive Ergebnisse auf Entzündungsmarker gezeigt, indem es den Vagusnerv moduliert. Einige Studien legen nahe, dass der Vagusnerv durch diesen Mechanismus die Anpassungsfähigkeit erhöhen und die Ansammlung von Beta-Amyloid im Gehirn und Plaque in den Arterien blockieren kann, was die Möglichkeit bietet, das Fortschreiten und die Schwere der Alzheimer-Krankheit zu verlangsamen und zu mildern.
Forschungsgestützte Evidenz von Nurosym
73% der Nutzer bemerkten eine verbesserte Kognition und Gedächtnis nach der Anwendung von Nurosym, was signifikante Verbesserungen der Demenzsymptome und der Gesamtproduktivität zeigt.
In klinischen Studien zeigten Patienten innerhalb von 5 Tagen eine 32%ige Verbesserung des Gedächtnisses und eine 26%ige Lernleistung mit Nurosym, was signifikante Verbesserungen sowohl in der Geschwindigkeit als auch in der Genauigkeit bei verschiedenen kognitiven Aufgaben im Vergleich zu Placebo zeigt.
Nach 2 Wochen Nurosym Neuromodulationstherapie erfuhren Patienten im Durchschnitt eine 57%ige Verbesserung der Kognition im Zusammenhang mit ME/CFS, wie in klinischen Studien belegt.
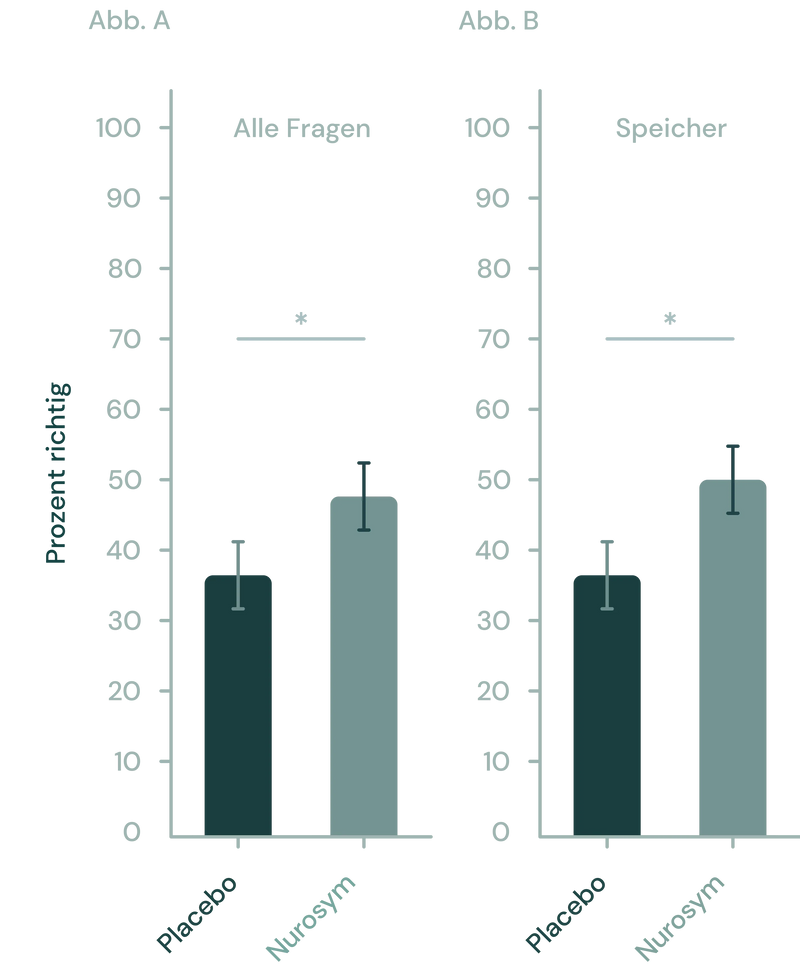
Nurosym hat gezeigt, dass es das Gedächtnis bei Lernaufgaben im Vergleich zu einem Placebo verbessert. (A) Über alle Testfragen hinweg zeigte die Neuromodulation von Nurosym einen bemerkenswerten Vorteil gegenüber dem Placebo. (B) Insbesondere war diese Verbesserung weitgehend auf den signifikanten Einfluss der Nurosym Neuromodulation auf gedächtnisbezogene Fragen zurückzuführen (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2020)
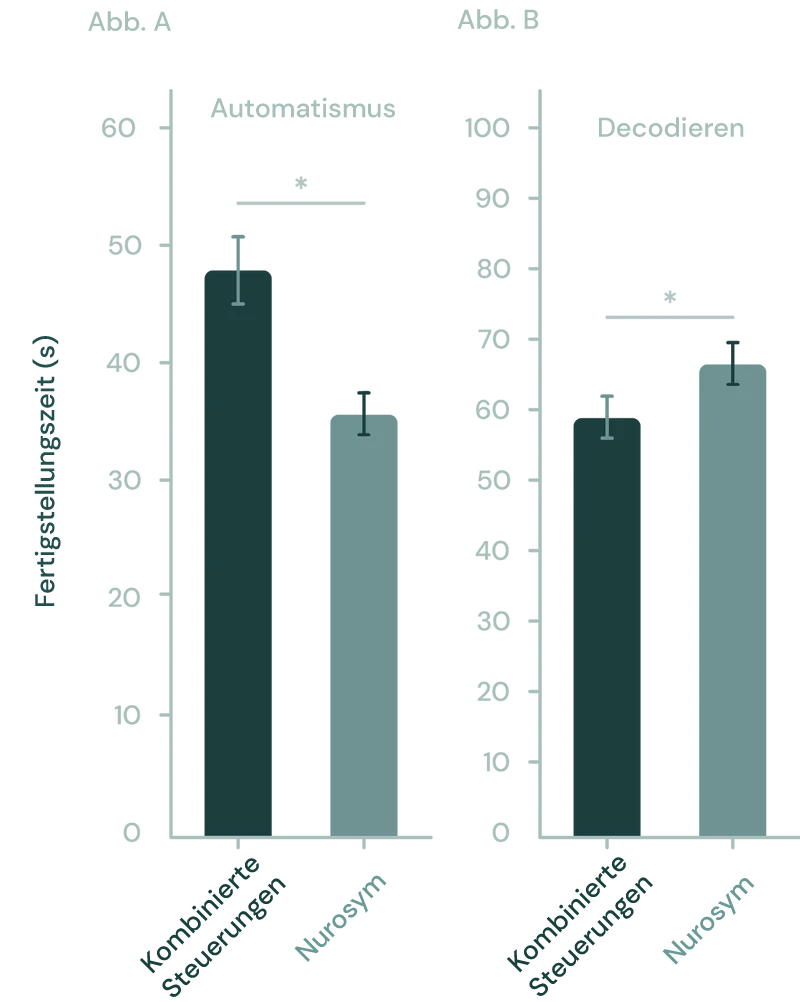
In der Studie verbesserte die Kombination von Nurosym Neuromodulation mit Training die Geschwindigkeit in der Automatisierungs-Lernaufgabe signifikant (*p<0.05) im Vergleich zu Placebo-Kontrollen. Zusätzlich verbesserte die Nurosym Neuromodulation signifikant die Genauigkeit, gemessen am Prozentsatz der richtigen Antworten, in der Dekodierungs-Lernaufgabe im Vergleich zu den Kontrollen (*p < 0,05) (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2020)
In klinischen Studien wurden die Teilnehmer zu drei wichtigen Zeitpunkten bewertet: Ausgangswert (Tag 0), nach der Intervention (Tag 10) und bei einer Nachuntersuchung nach einem Monat. Die Intervention führte zu signifikanten kognitiven Verbesserungen, wobei die Leistung in der Flanker-Inhibitionskontrolle und Aufmerksamkeit um 11 % und die gesamte Flüssige Kognition um 17 % zunahm.
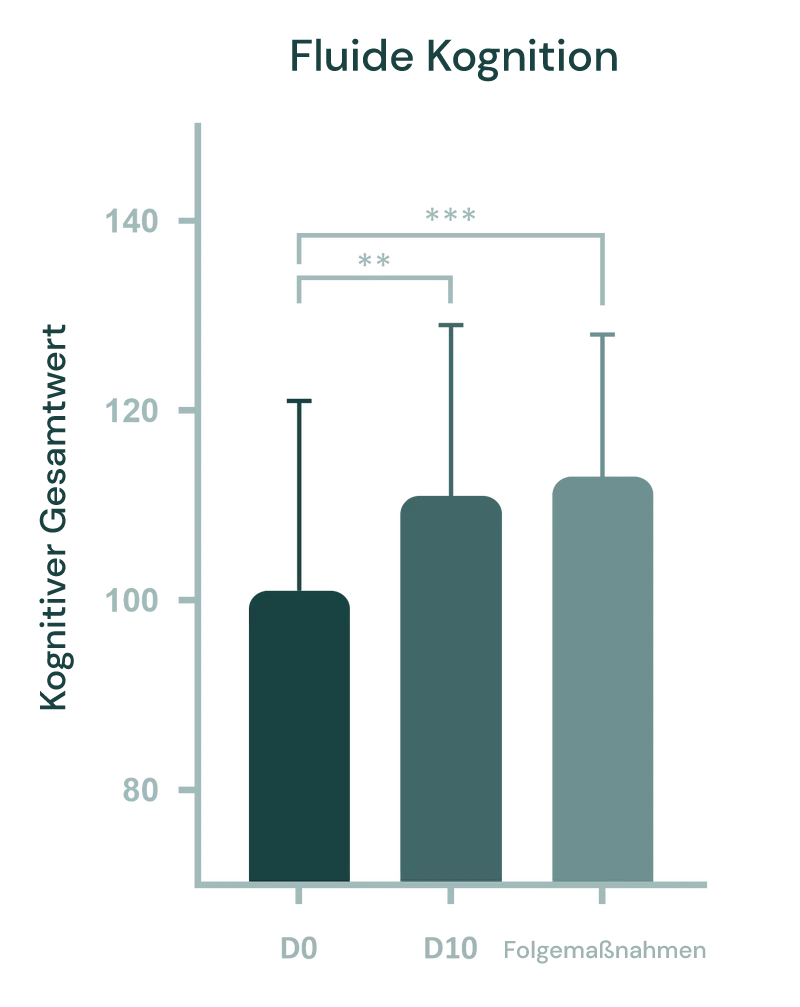
(Abb.). Der Flüssige Kognitionswert repräsentiert die kognitive Leistung in mehreren Bereichen, einschließlich Verarbeitungsgeschwindigkeit beim Mustervergleich, Mustersequenzierungsgedächtnis und Arbeitsgedächtnis beim Listensortieren. Die Studie zeigte signifikante Zunahmen vom Ausgangswert bis zur Nachuntersuchung und Nachverfolgung (p < 0,01). Der Friedman-Test zeigte einen signifikanten Haupteffekt der Zeit (p = 0,001) über alle zusammengesetzten kognitiven Werte hinweg.
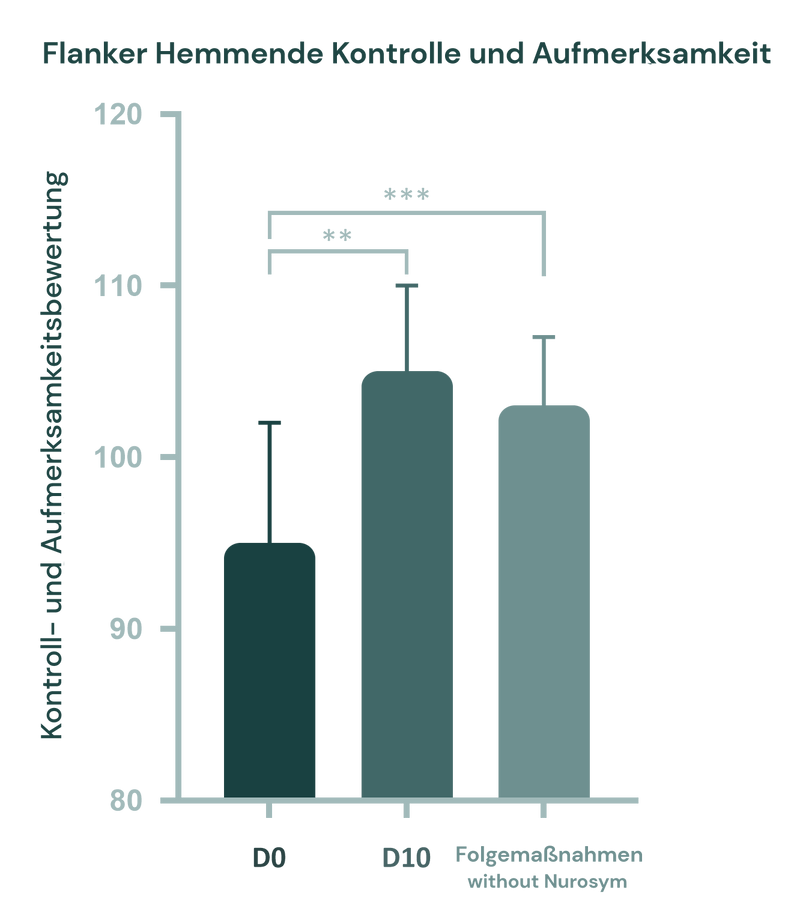
(Abb.). Die Teilnehmer wurden zu drei Zeitpunkten getestet: Ausgangswert (Tag 0), nach der Intervention (Tag 10) und Nachuntersuchung nach einem Monat. Signifikante Verbesserungen wurden in der Flanker-Inhibitionskontrolle und Aufmerksamkeit vom Ausgangswert bis zur Nachuntersuchung (p = 0,009) und Nachverfolgung (p < 0,001) festgestellt.
In klinischen Studien erlebten Patienten nach Nurosym Neuromodulation einen Rückgang der Neuropeptidspiegel (wie NPY) um 38 %, was auf verminderte neurogene Entzündungsprozesse im Gehirn hinweist. Diese Reduktion ist mit einem Rückgang neurodegenerativer Prozesse und Stressreaktionen verbunden.
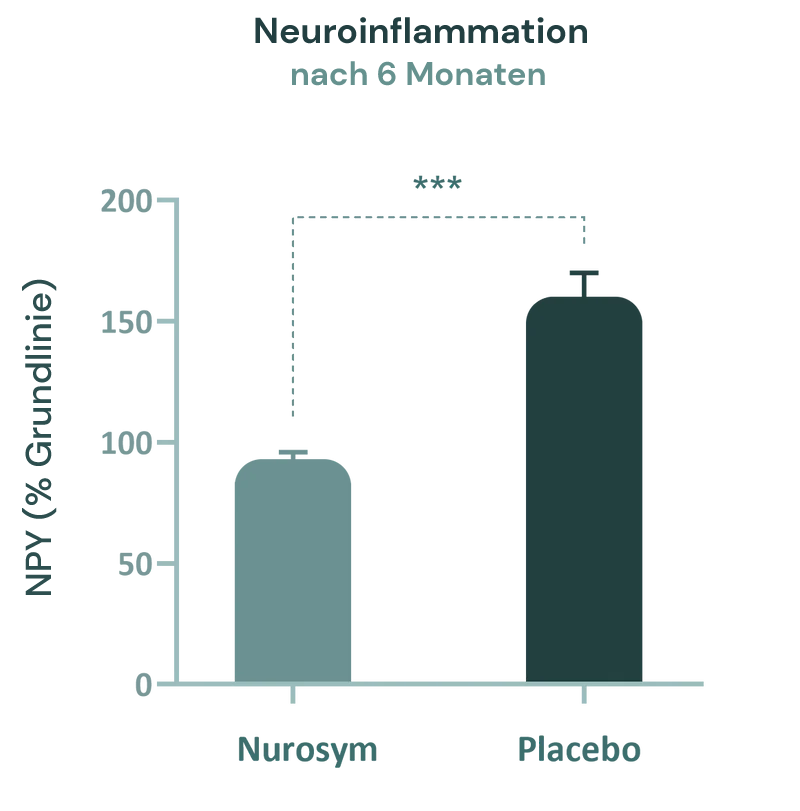
*Abb). Ein bemerkenswerter Rückgang der zirkulierenden Neuropeptid Y (NPY)-Spiegel wurde nach 6 Monaten Nurosym-Behandlung beobachtet. NPY ist mit dem Risiko mehrerer kognitiver Störungen verbunden (Parasym Clinical Trials, 2020).
Erhöhte Spiegel reaktiver Sauerstoffspezies (ROS) sind mit neurodegenerativen Erkrankungen verbunden. Nurosym senkte die ROS-Marker um ~24 %, was Neuronen schützen und möglicherweise das Fortschreiten von Erkrankungen wie Alzheimer und Parkinson verlangsamen könnte.
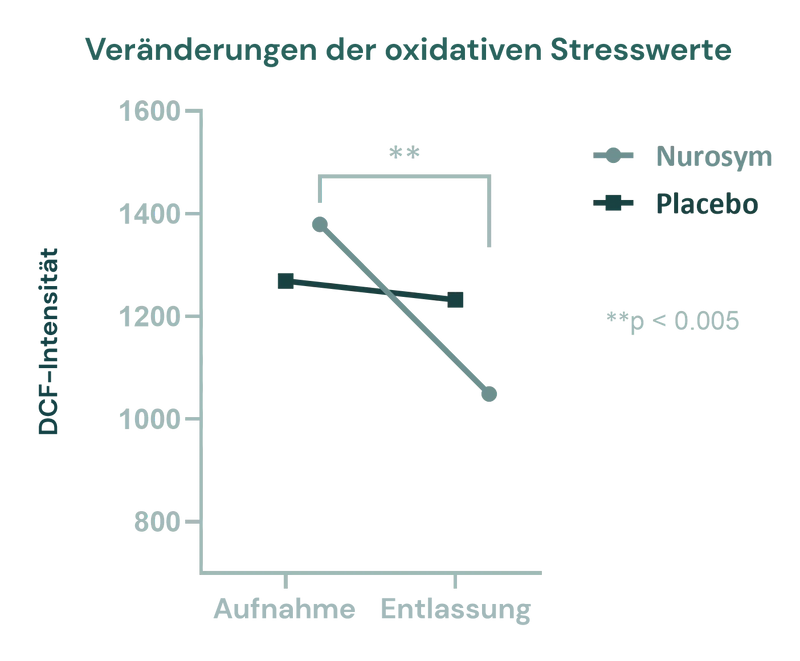
Abb. Auswirkung von LLTS auf oxidativen Stress. Eine Veränderung der Medianwerte von DCF vom Eintritt bis zur Entlassung in der Nurosym-Gruppe im Vergleich zur Kontroll-Placebo-Gruppe (Parasym Clinical Trial, 2023)
Ärzte über Nurosym
Patienten über Nurosym
Yvonne
„Ich benutze das Nurosym-Gerät seit Januar 2021. Ich benutze es jeden Tag eine Stunde lang und manchmal erreiche ich sogar noch mehr Konzentration. Manchmal lese ich ein Buch, während ich es trage. Und ich finde, dass ich mich manchmal auf ziemlich schwierige Texte konzentrieren kann.“
Für wen ist es geeignet?
Nurosym bietet erhebliche Vorteile für diejenigen, die kognitiven Abbau verhindern, verlangsamen oder sogar umkehren und das Gedächtnis verbessern möchten. Im Bereich komplexer, mit Demenz verbundener Erkrankungen, bei denen bestimmte Medikamente potenzielle Nebenwirkungen haben können, erweist sich die Neuromodulationstherapie wie das Nurosym-Gerät als vielversprechende und nicht-invasive Option.
Darüber hinaus erweist es sich als wertvoll für Patienten, die sich von Hirnverletzungen erholen, da Nurosym eine entscheidende Rolle bei der signifikanten Verbesserung der Blutversorgung des Gehirns spielt.
Protokoll - Anwendungshinweise
Personen mit kognitiven Beeinträchtigungen können potenziell vom Nurosym-Gerät profitieren, indem sie das Gerät täglich zwei Stunden lang nutzen, aufgeteilt in vier 30-minütige Sitzungen. Beginnen Sie jede Sitzung 5 Minuten, bevor Sie an kognitiven Aktivitäten wie Gedächtnisspielen, Lesen oder Puzzles teilnehmen, um die kognitive Funktion zu optimieren.
Für Patienten nach Hirnverletzungen, insbesondere solche mit motorischen Beeinträchtigungen und Gefäßproblemen: Integrieren Sie das Nurosym-Gerät bis zu vier Stunden täglich, aufgeteilt in vier 60-minütige Sitzungen, um die Gehirngesundheit und zugrunde liegende Bedingungen zu unterstützen. Starten Sie jede Sitzung 5 Minuten, bevor Sie mit Physiotherapie oder Übungen beginnen, um potenziell das motorische Lernen zu verbessern und den Erholungsprozess zu unterstützen.
Wie oft
Nurosym wird basierend auf klinischer Forschung und Patientenfeedback zur zweimal täglichen Anwendung empfohlen. Dieses Regime sorgt für eine optimale Energieausbalancierung und Beruhigung des Nervensystems.
Wie lange
Benutzer sollten 30 Minuten am Morgen und 60 Minuten vor dem Schlafengehen für Nurosym-Therapie-Sitzungen einplanen. Konsistenz in der Anwendung ist der Schlüssel, um die gewünschten Ergebnisse zu erzielen.
Ergebnisse
Positive Ergebnisse der Nurosym-Therapie können innerhalb eines relativ kurzen Zeitraums bemerkbar werden. Viele Personen berichten von Verbesserungen innerhalb weniger Tage nach Beginn der Behandlung.


